Science - online puzzles
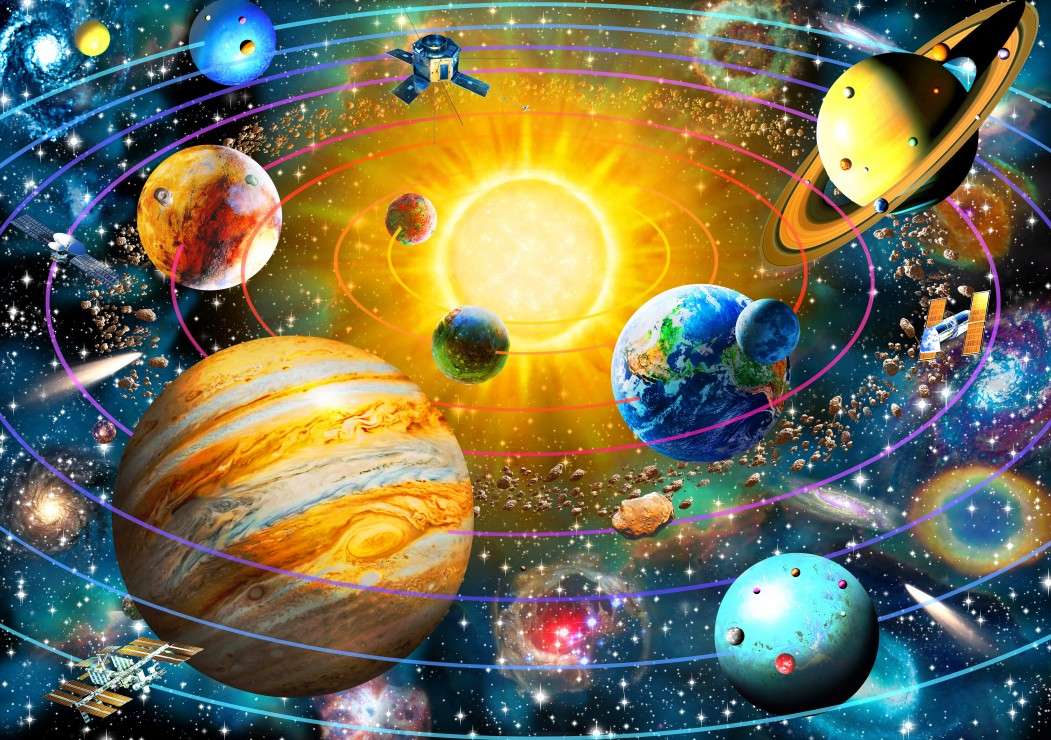
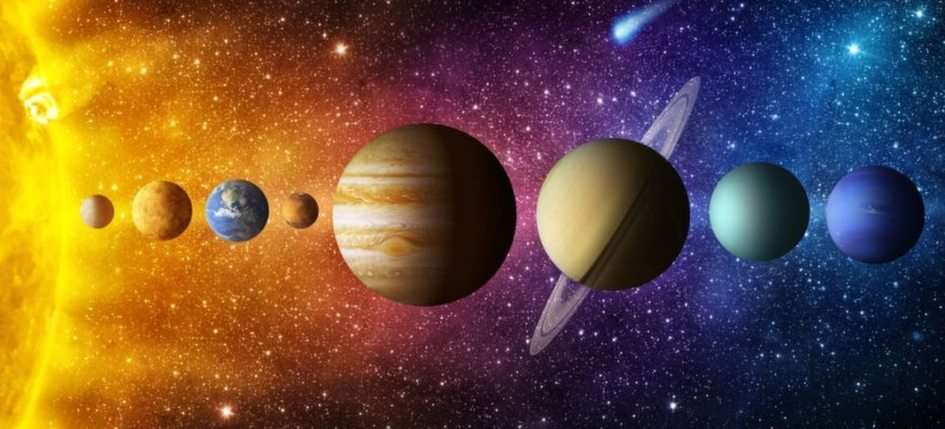
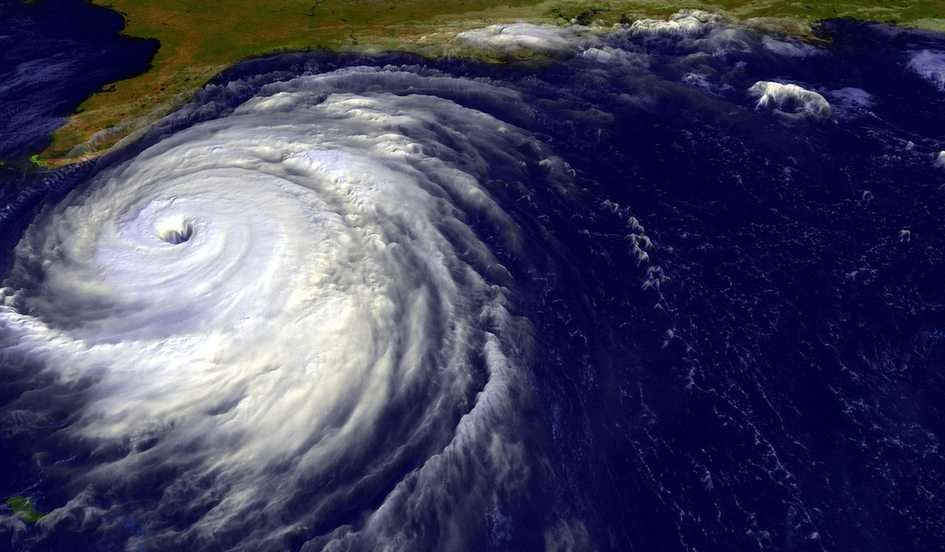













































Online puzzle Science
Science
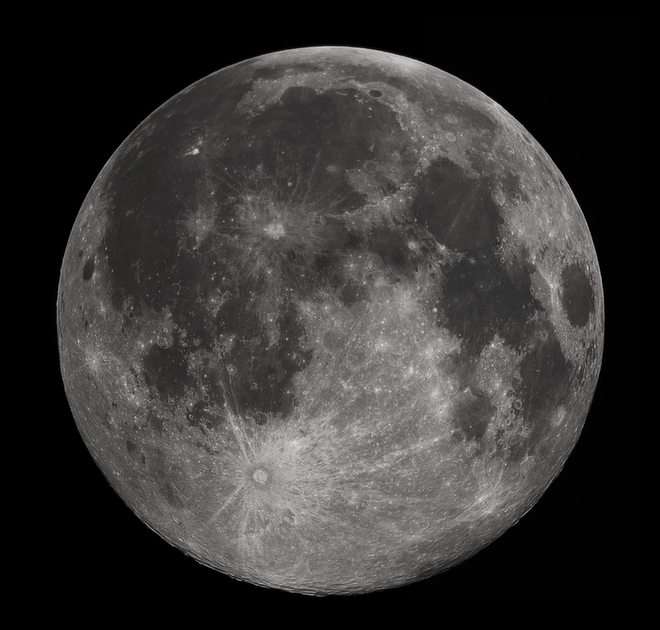
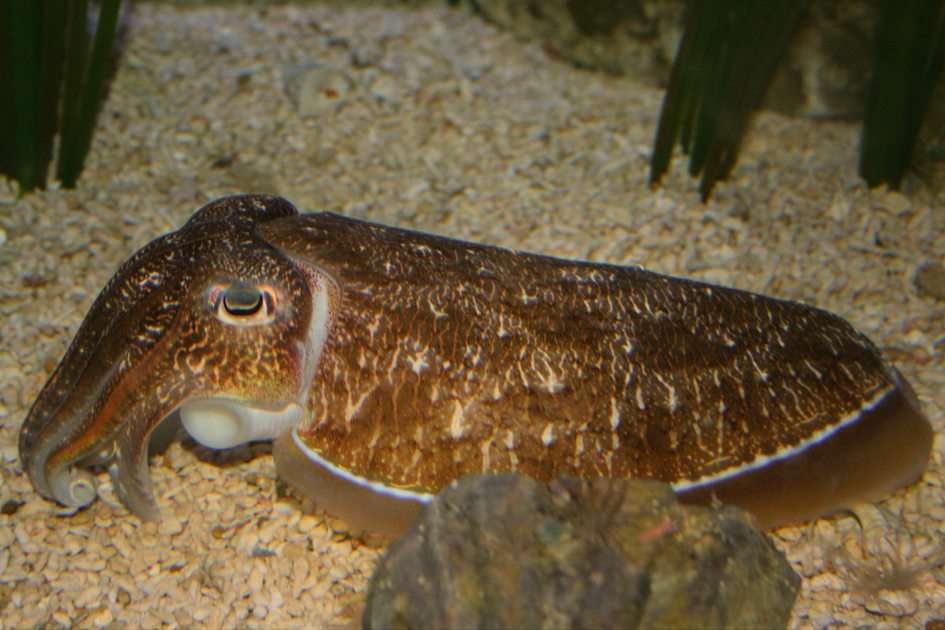
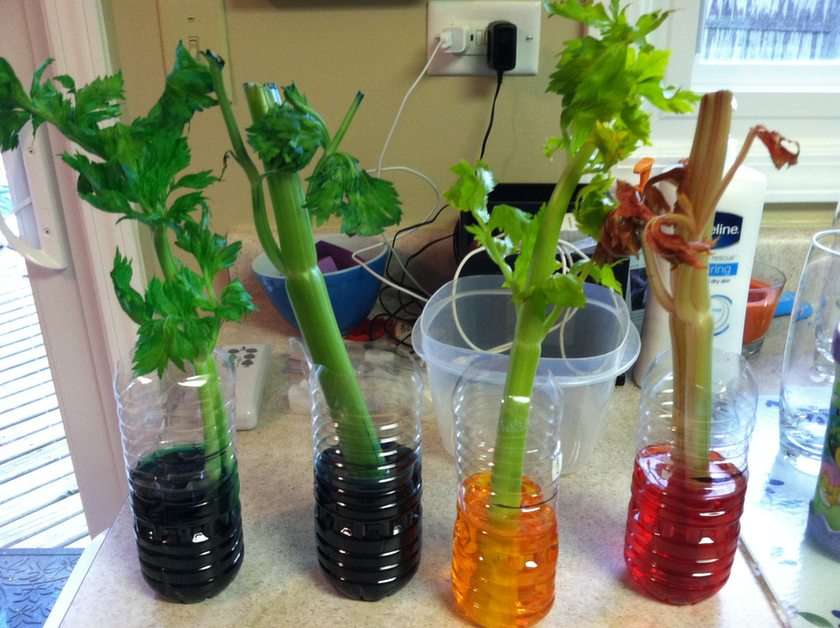
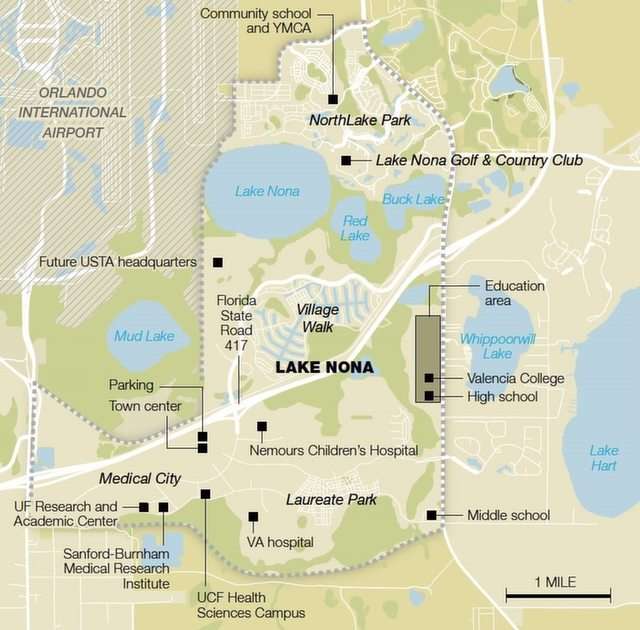
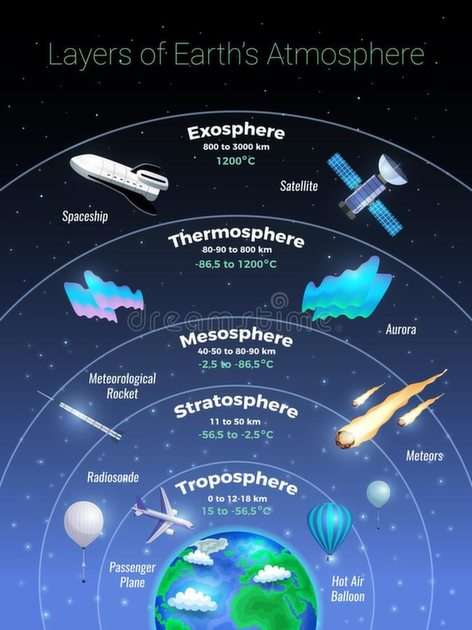
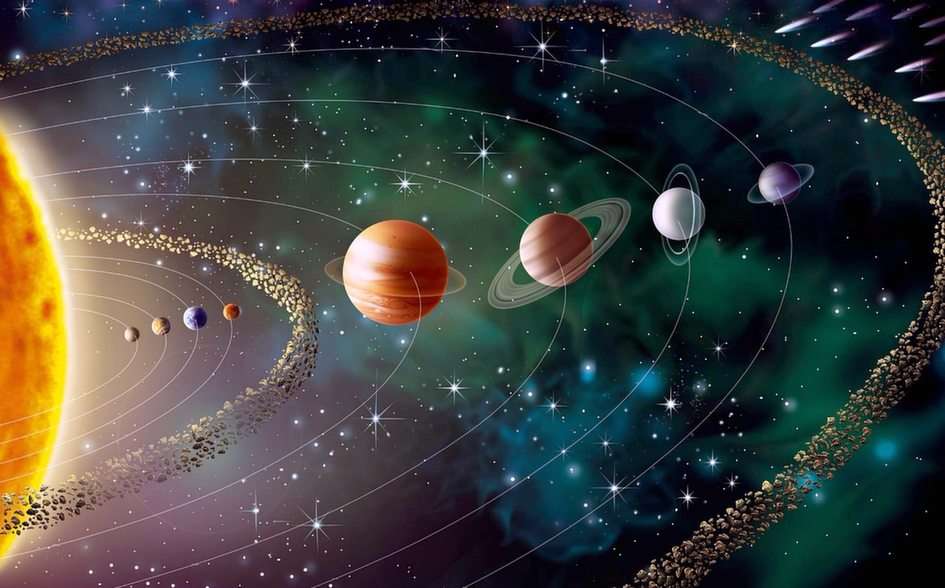
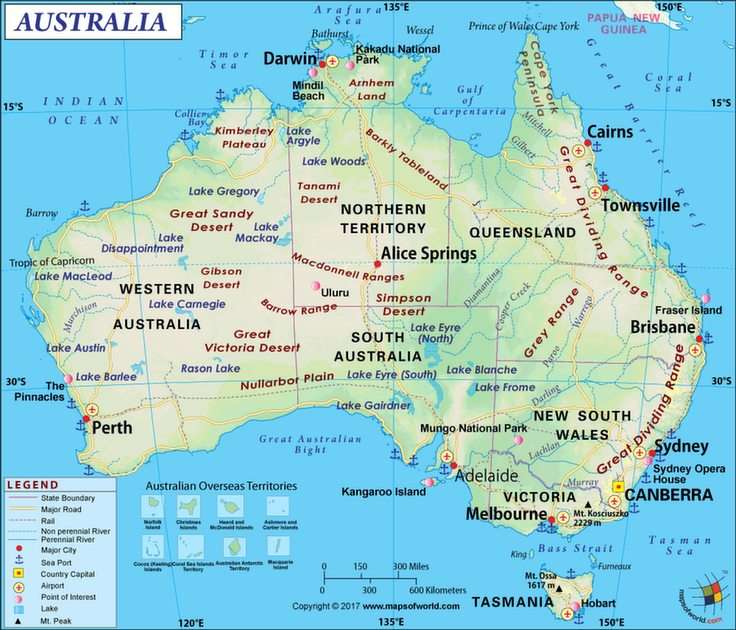
Science is a neutral, rigorous, systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into three major branches: natural sciences (e.g., biology, chemistry, and physics), which study the physical world; the social sciences (e.g., economics, psychology, and sociology), which study individuals and societies; and the formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science), which study formal systems, governed by axioms and rules. There is disagreement whether the formal sciences are science disciplines, because they do not rely on empirical evidence. Applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as in engineering and medicine.The history of scientific discipline spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest written records of identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to Bronze Age Egypt and Mesopotamia from around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes, while further advancements, including the introduction of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, were made during the Golden Age of India.: 12 Scientific research deteriorated in these regions after the fall of the Western Roman Empire and Gupta empire during the early middle ages (400 to 1000 CE,) but was preserved and expanded upon in the Middle East during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek manuscripts from the dying Byzantine Empire to Western Europe in the Renaissance.
The recovery and assimilation of Greek works and Islamic inquiries into Western Europe from the 10th to 13th century revived "natural philosophy", which was later transformed by the Scientific Revolution that began in the 16th century as new ideas and discoveries departed from previous Greek conceptions and traditions. The scientific method soon played a greater role in knowledge creation and it was not until the 19th century that many of the institutional and professional features of science began to take shape, along with the changing of "natural philosophy" to "natural science".New knowledge in science is advanced by research from scientists who are motivated by curiosity about the world and a desire to solve problems. Contemporary scientific research is highly collaborative and is usually done by teams in academic and research institutions, government agencies, and companies. The practical impact of their work has led to the emergence of science policies that seek to influence the scientific enterprise by prioritizing the ethical and moral development of commercial products, armaments, health care, public infrastructure, and environmental protection.