Animal - online puzzles






















































Online puzzle Animal
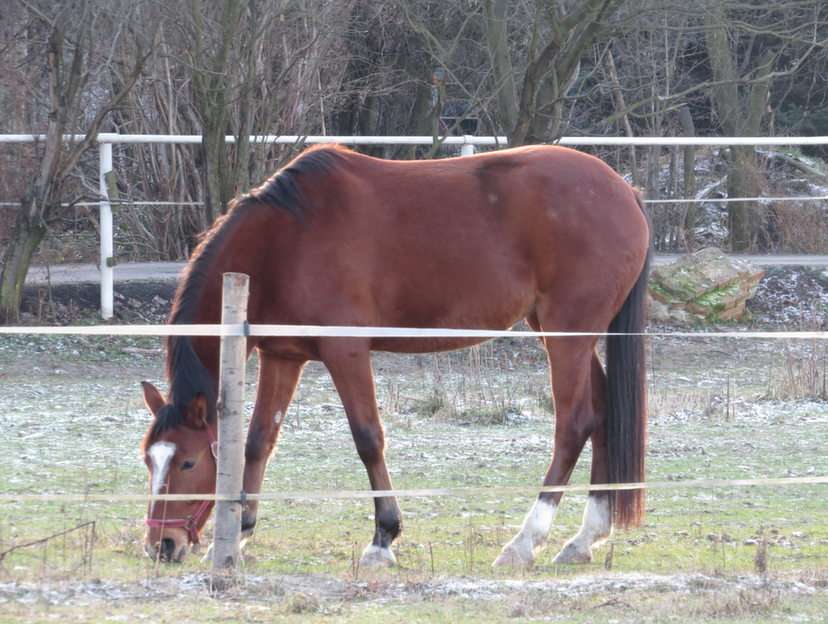
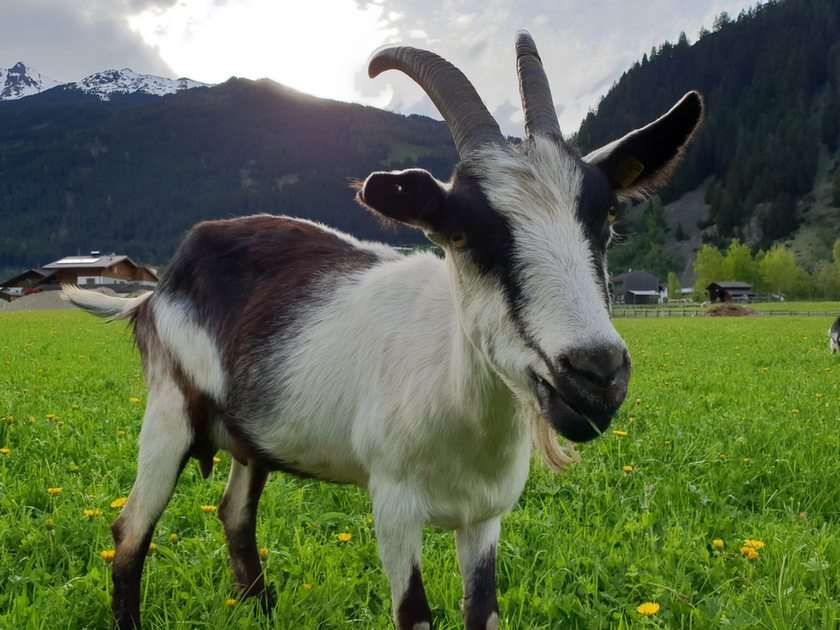
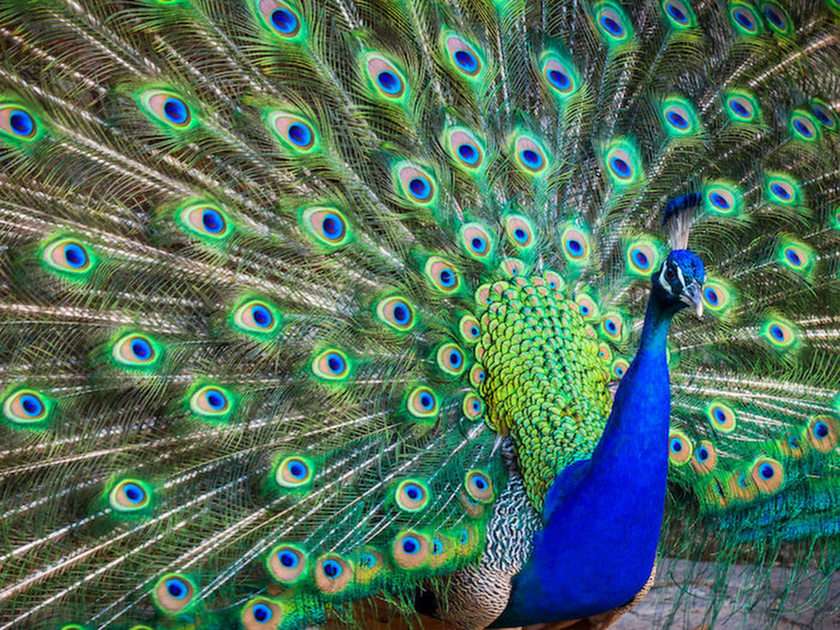
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. As of 2022, 2.16 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates—but it has been estimated there are around 7.77 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from 8.5 micrometres (0.00033 in) to 33.6 metres (110 ft). They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology.
Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms and the chordates, the latter including the vertebrates. Life forms interpreted as early animals were present in the Ediacaran biota of the late Precambrian. Many modern animal phyla became clearly established in the fossil record as marine species during the Cambrian explosion, which began around 539 million years ago. 6,331 groups of genes common to all living animals have been identified; these may have arisen from a single common ancestor that lived 650 million years ago.
Historically, Aristotle divided animals into those with blood and those without. Carl Linnaeus created the first hierarchical biological classification for animals in 1758 with his Systema Naturae, which Jean-Baptiste Lamarck expanded into 14 phyla by 1809. In 1874, Ernst Haeckel divided the animal kingdom into the multicellular Metazoa (now synonymous with Animalia) and the Protozoa, single-celled organisms no longer considered animals. In modern times, the biological classification of animals relies on advanced techniques, such as molecular phylogenetics, which are effective at demonstrating the evolutionary relationships between taxa.
Humans make use of many animal species, such as for food (including meat, milk, and eggs), for materials (such as leather and wool), as pets, and as working animals including for transport. Dogs have been used in hunting, as have birds of prey, while many terrestrial and aquatic animals were hunted for sports. Nonhuman animals have appeared in art from the earliest times and are featured in mythology and religion.