Mammal - online puzzles
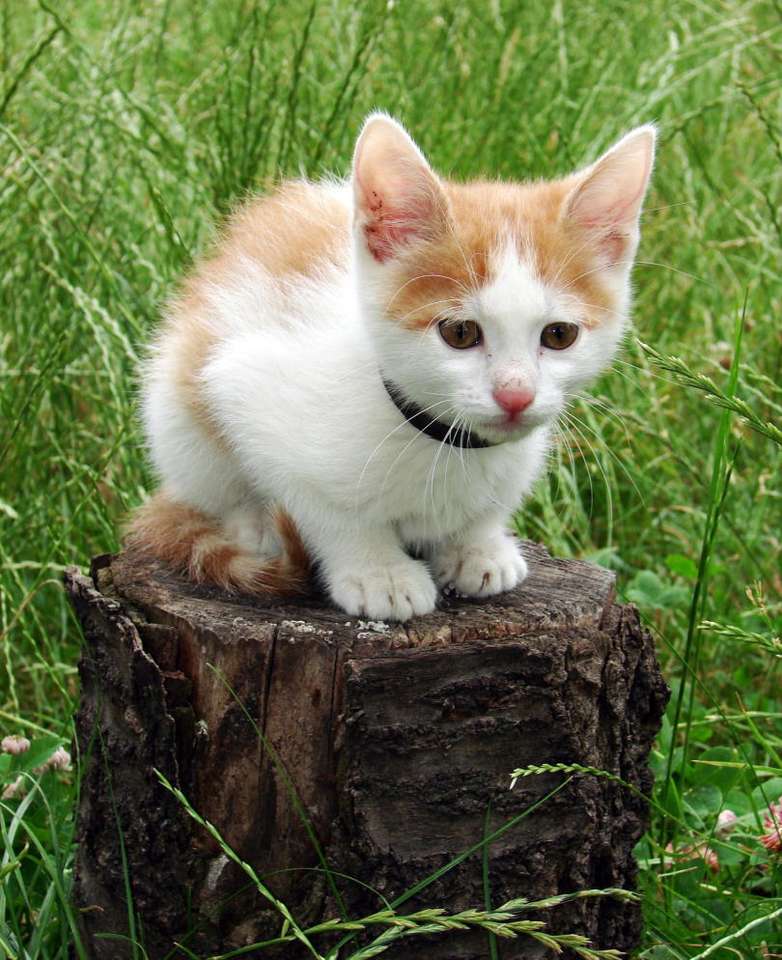
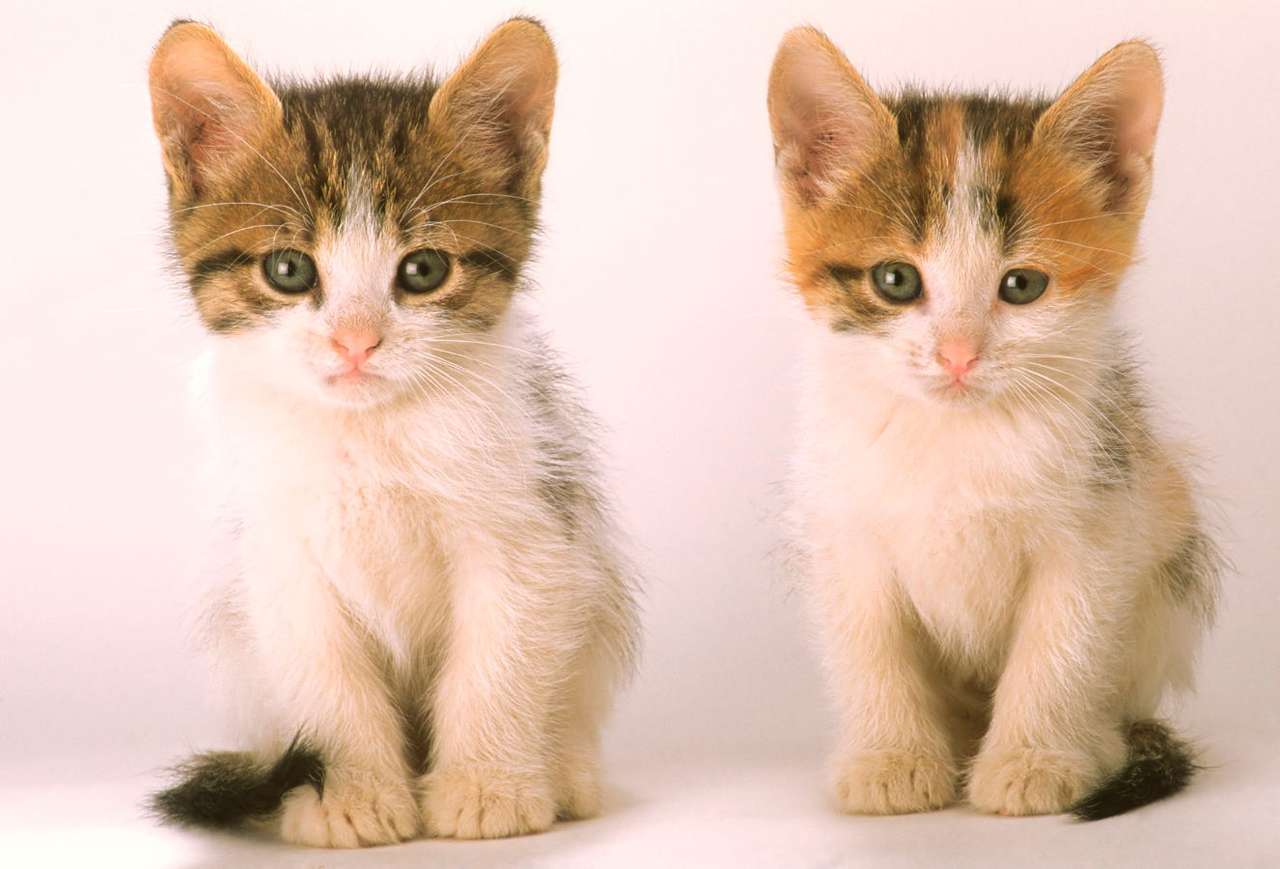
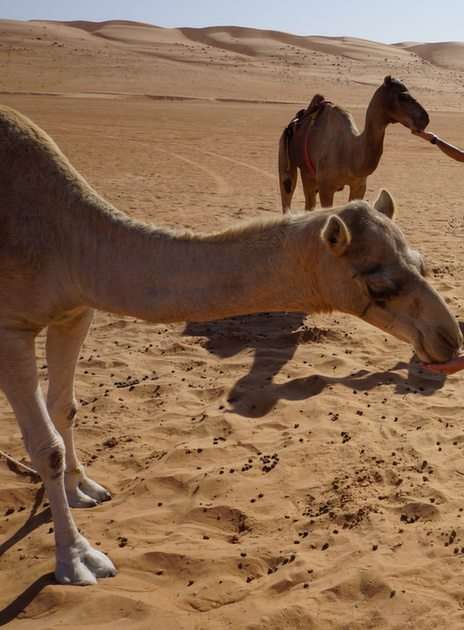
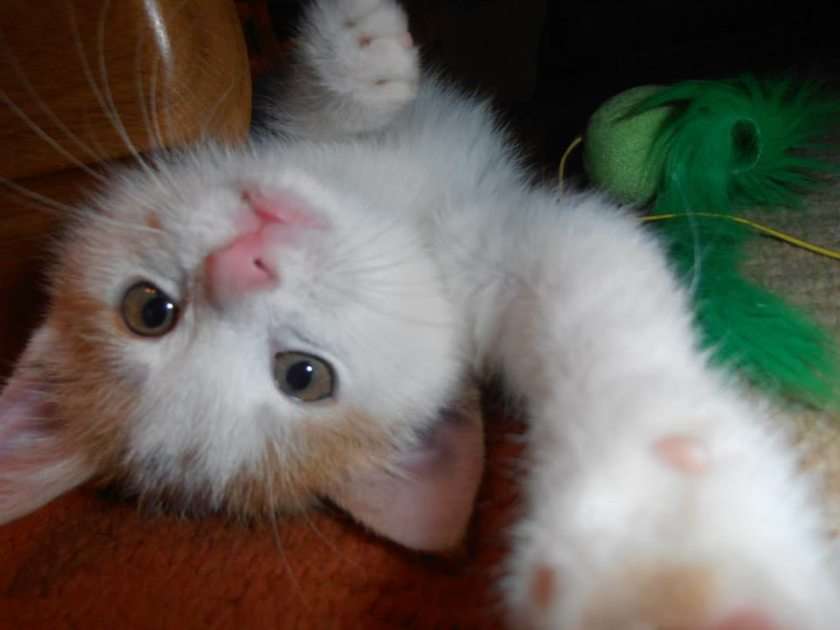
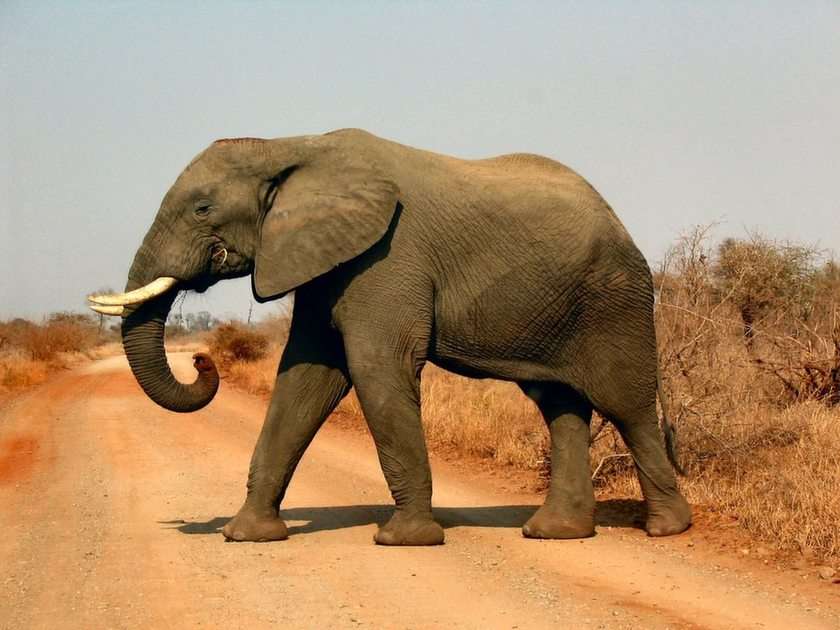





















































Online puzzle Mammal
Mammal
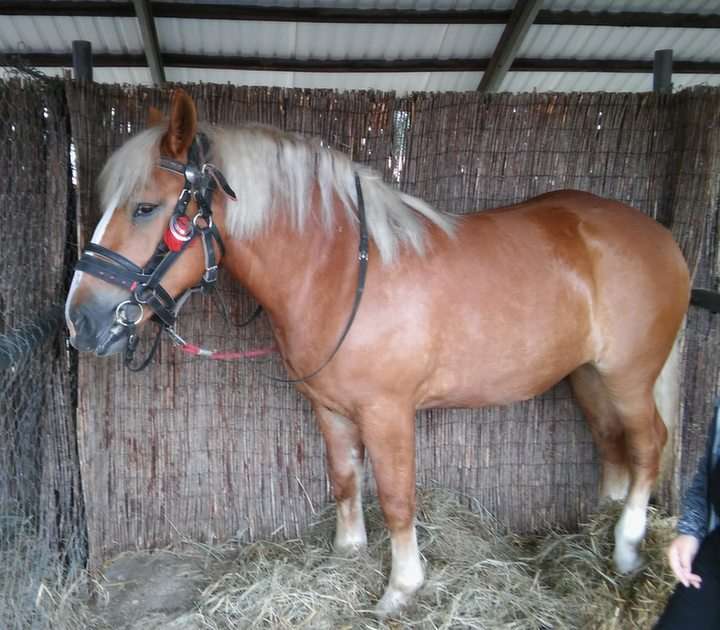
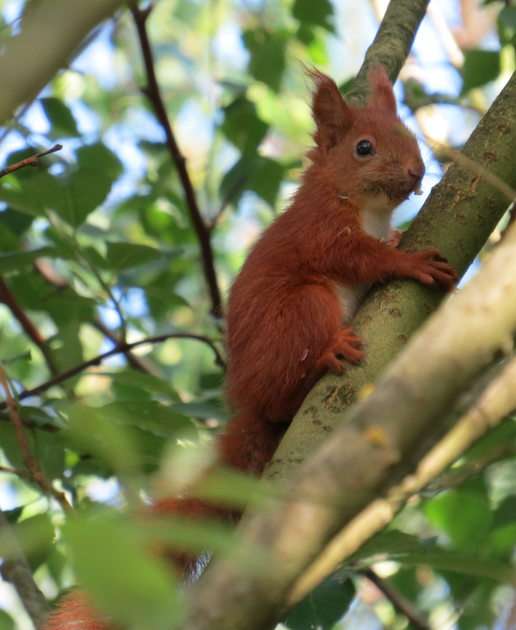
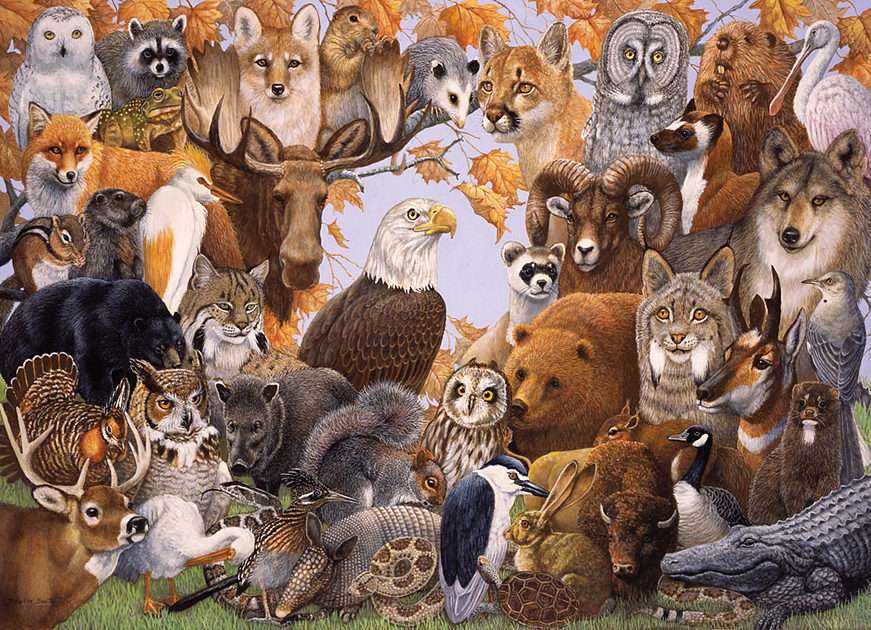
A mammal (from Latin mamma 'breast') is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterized by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 29 orders.
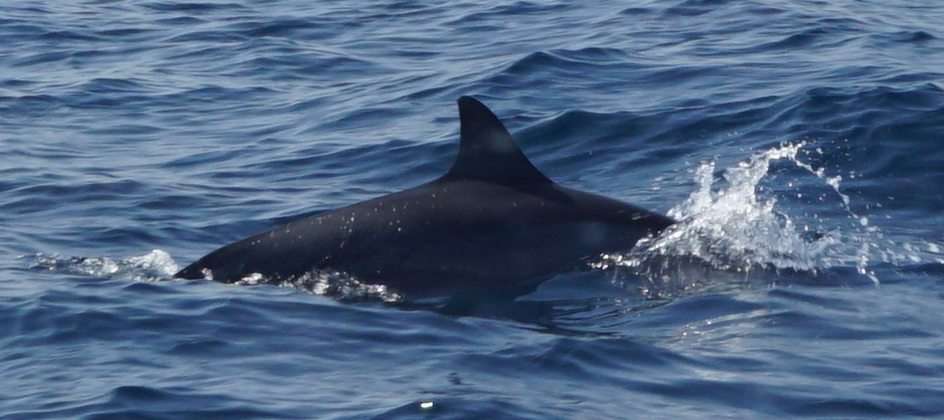
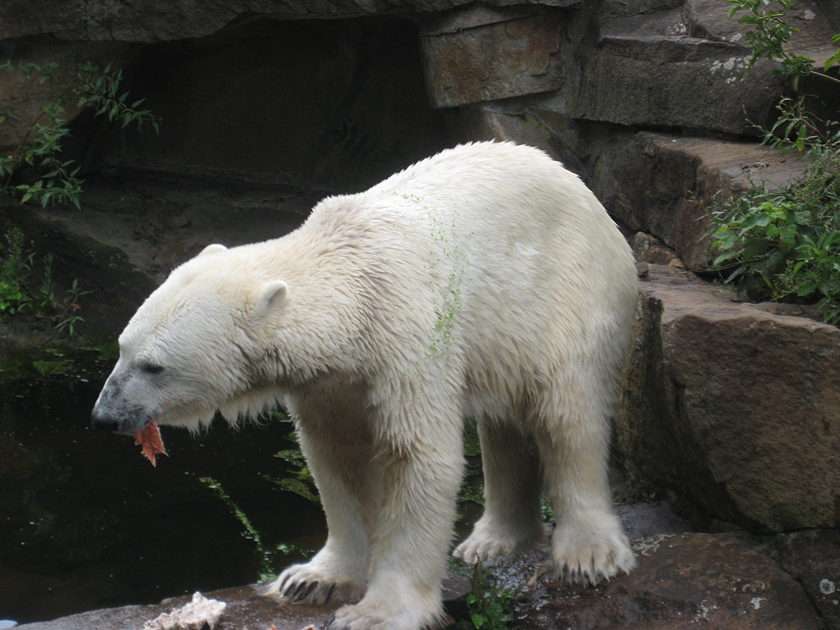
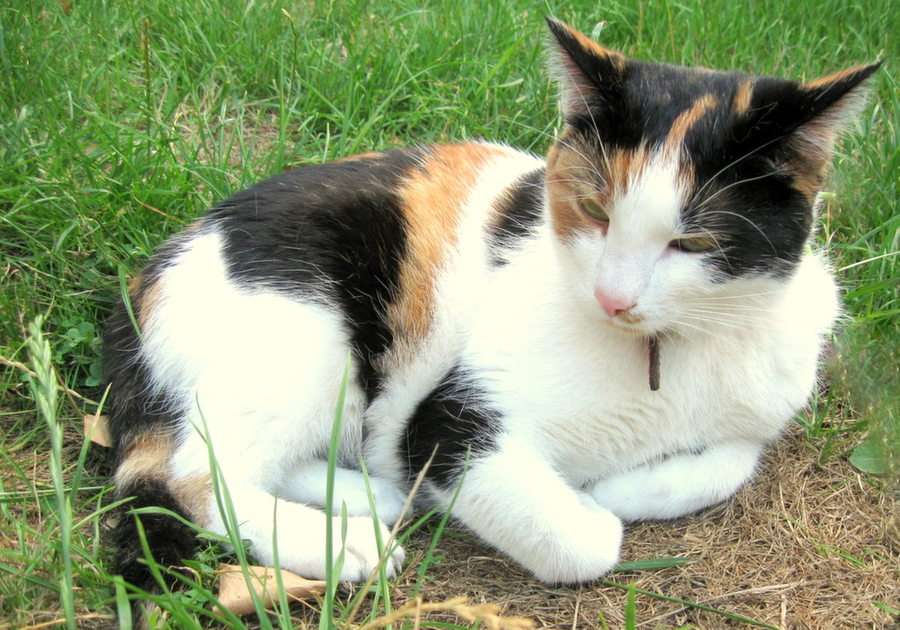
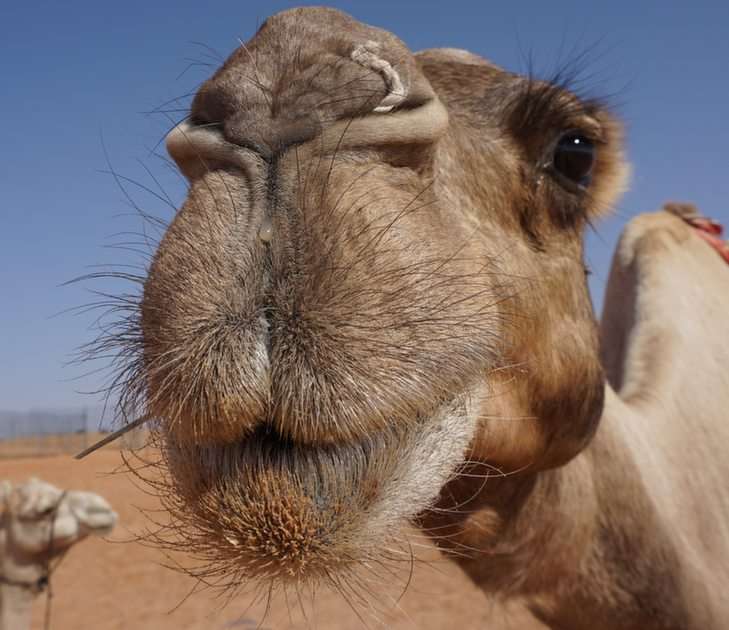
The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (including hedgehogs, moles and shrews). The next three are the Primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including cats, dogs, and seals).
Mammals are the only living members of Synapsida; this clade, together with Sauropsida (reptiles and birds), constitutes the larger Amniota clade. The early synapsids were sphenacodonts, a group that included the famous Dimetrodon. The synapsids split into several diverse groups of non-mammalian synapsids—traditionally and incorrectly referred to as mammal-like reptiles or by the term pelycosaurs, and now known as stem mammals or protomammals—before giving rise to therapsids during the beginning of the Middle Permian period. Mammals originated from cynodonts, an advanced group of therapsids, during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic. The modern mammalian orders arose in the Paleogene and Neogene periods of the Cenozoic era, after the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs, and have been the dominant terrestrial animal group from 66 million years ago to the present.
The basic mammalian body type is quadruped, and most mammals use their four extremities for terrestrial locomotion; but in some, the extremities are adapted for life at sea, in the air, in trees, underground, or on two legs. Mammals range in size from the 30–40 mm (1.2–1.6 in) bumblebee bat to the 30 m (98 ft) blue whale—possibly the largest animal to have ever lived. Maximum lifespan varies from two years for the shrew to 211 years for the bowhead whale. All modern mammals give birth to live young, except the five species of monotremes, which are egg-laying mammals. The most species-rich group of mammals, the cohort called placentals, have a placenta, which enables the feeding of the fetus during gestation.
Most mammals are intelligent, with some possessing large brains, self-awareness, and tool use. Mammals can communicate and vocalize in several ways, including the production of ultrasound, scent-marking, alarm signals, singing, echolocation; and, in the case of humans, complex language. Mammals can organize themselves into fission-fusion societies, harems, and hierarchies—but can also be solitary and territorial. Most mammals are polygynous, but some can be monogamous or polyandrous.
Domestication of many types of mammals by humans played a major role in the Neolithic Revolution, and resulted in farming replacing hunting and gathering as the primary source of food for humans. This led to a major restructuring of human societies from nomadic to sedentary, with more co-operation among larger and larger groups, and ultimately the development of the first civilizations. Domesticated mammals provided, and continue to provide, power for transport and agriculture, as well as food (meat and dairy products), fur, and leather. Mammals are also hunted and raced for sport, and are used as model organisms in science. Mammals have been depicted in art since Paleolithic times, and appear in literature, film, mythology, and religion. Decline in numbers and extinction of many mammals is primarily driven by human poaching and habitat destruction, primarily deforestation.