Star - online puzzles

















































Online puzzle Star
Star
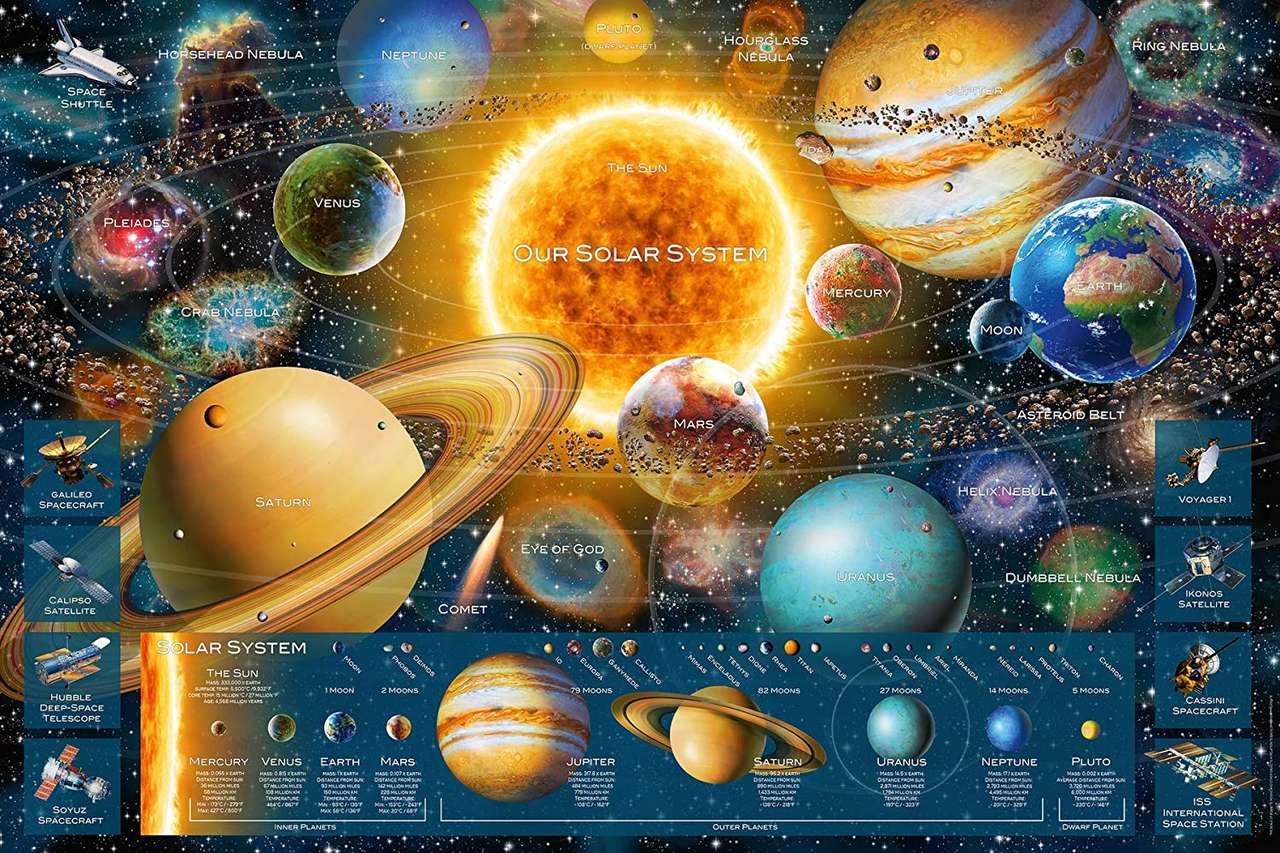
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated 1022 to 1024 stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy.
A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its total mass is the main factor determining its evolution and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates into outer space. At the end of a star's lifetime, its core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole.
Stellar nucleosynthesis in stars or their remnants creates almost all naturally occurring chemical elements heavier than lithium. Stellar mass loss or supernova explosions return chemically enriched material to the interstellar medium. These elements are then recycled into new stars. Astronomers can determine stellar properties—including mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), variability, distance, and motion through space—by carrying out observations of a star's apparent brightness, spectrum, and changes in its position in the sky over time.
Stars can form orbital systems with other astronomical objects, as in the case of planetary systems and star systems with two or more stars. When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can significantly impact their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy.