Fungus - online puzzles
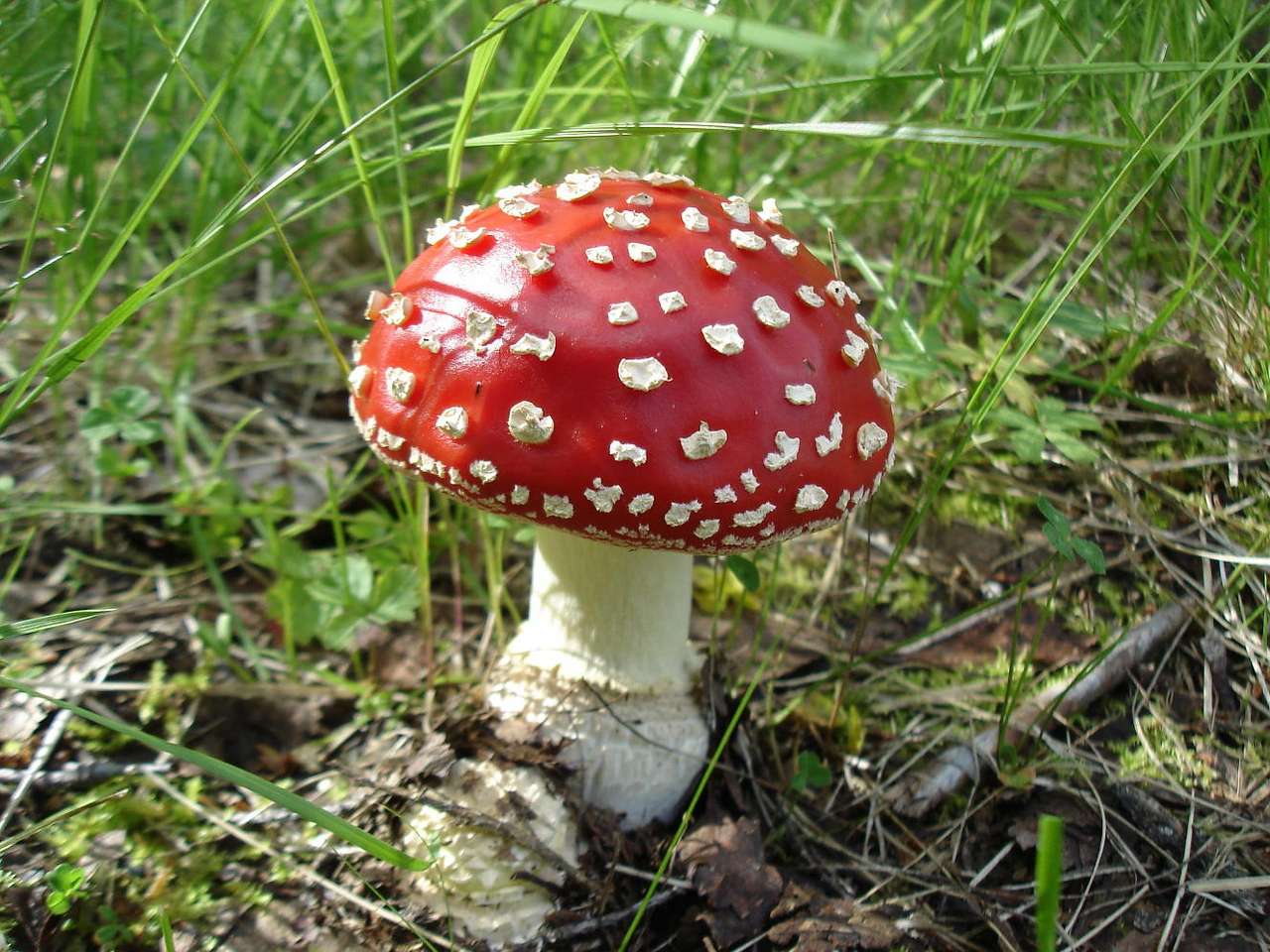
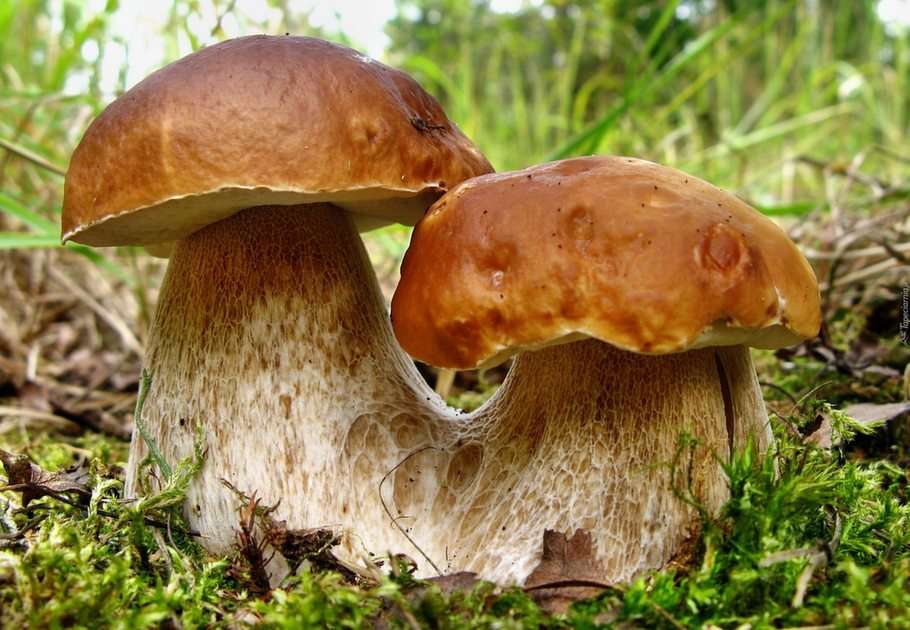
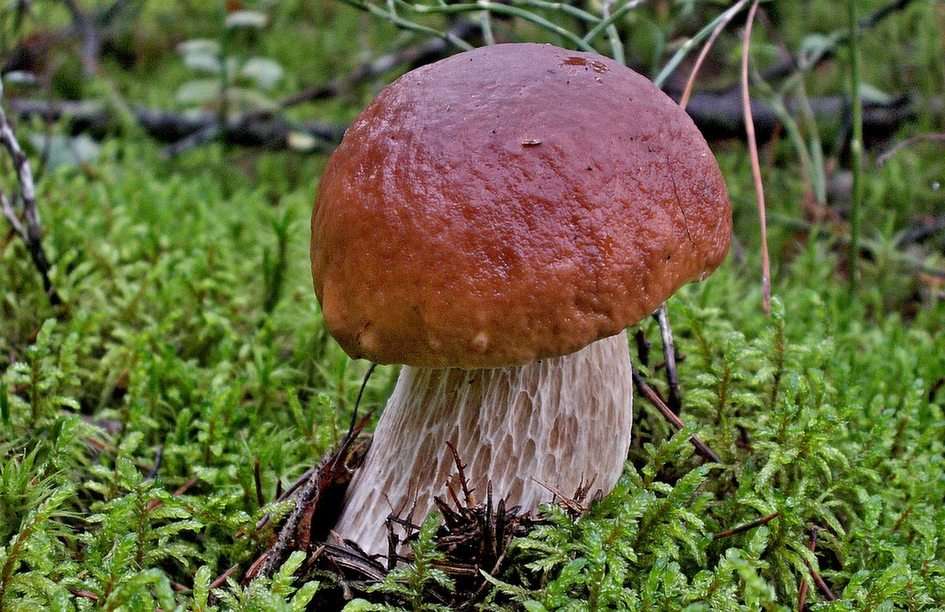
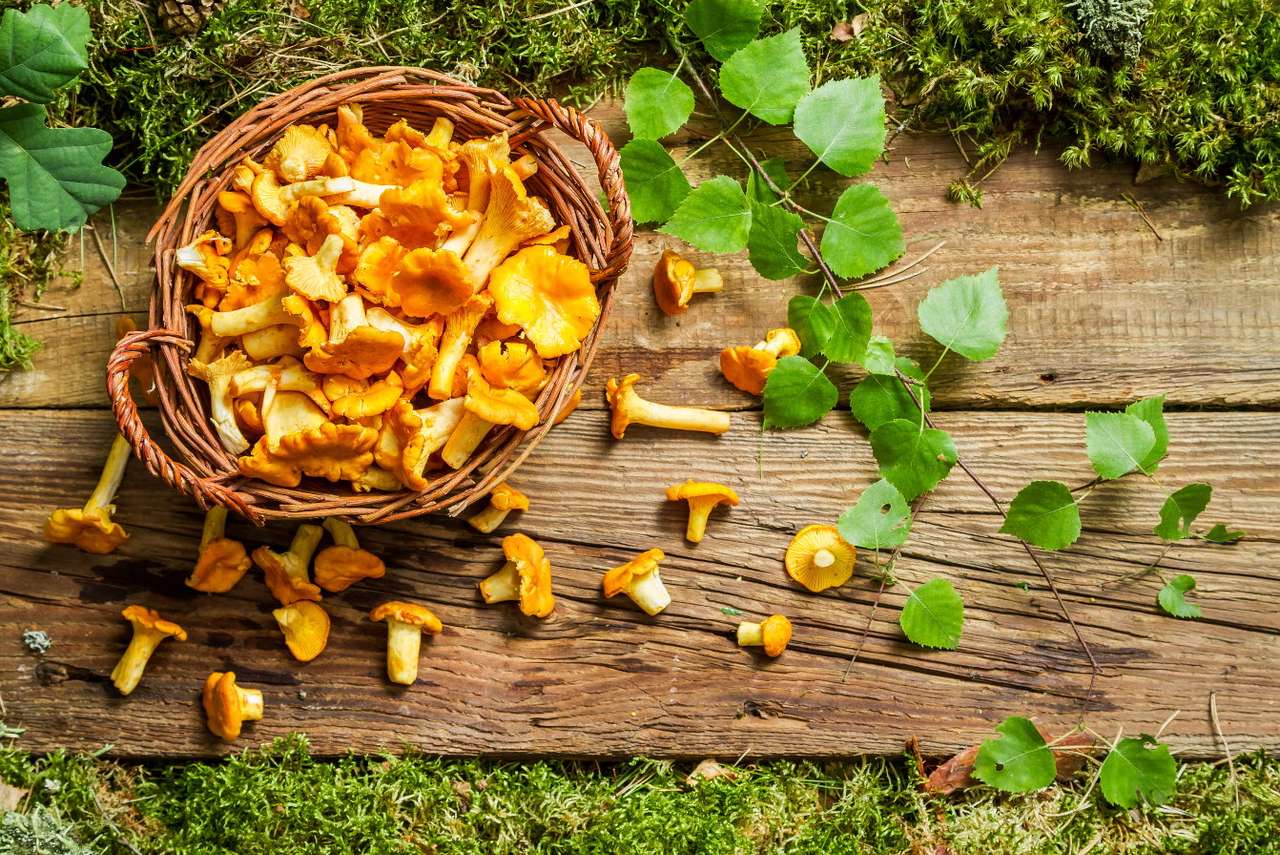
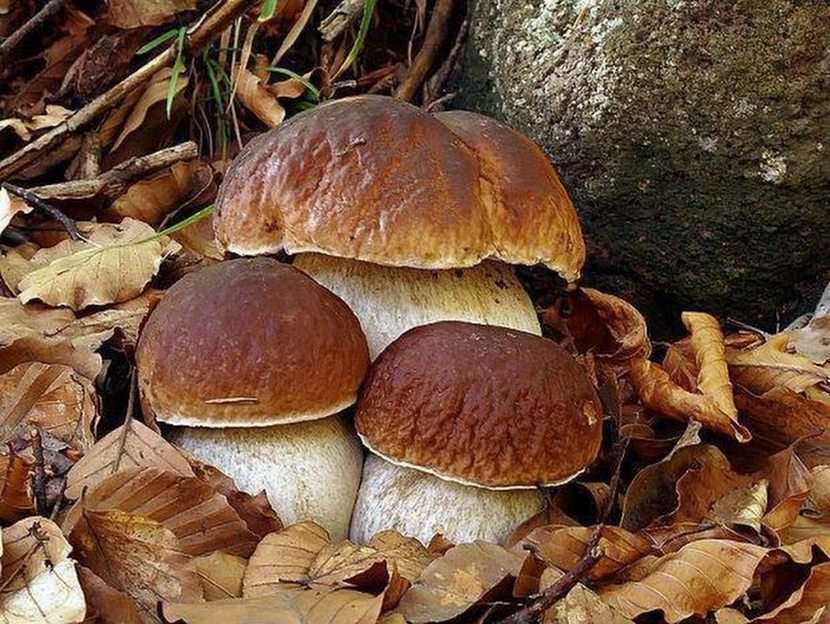
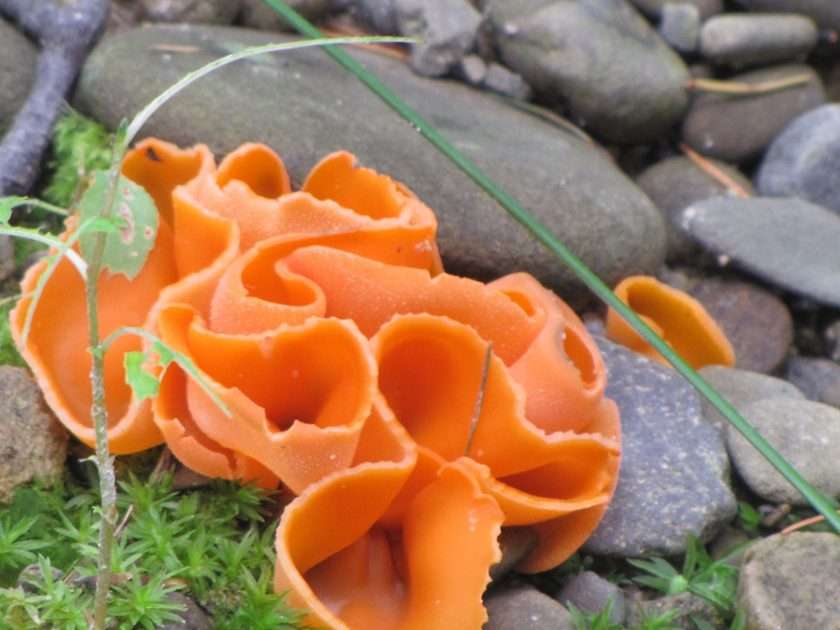
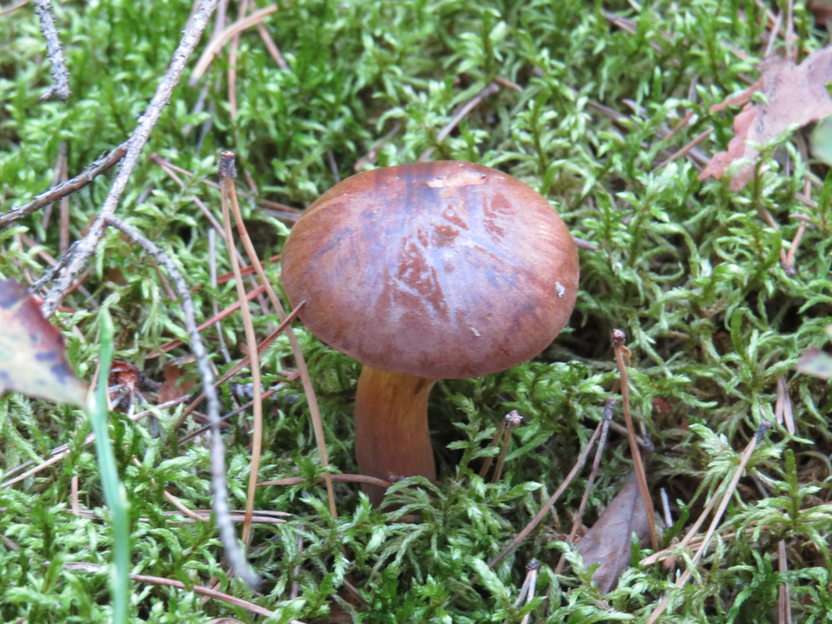
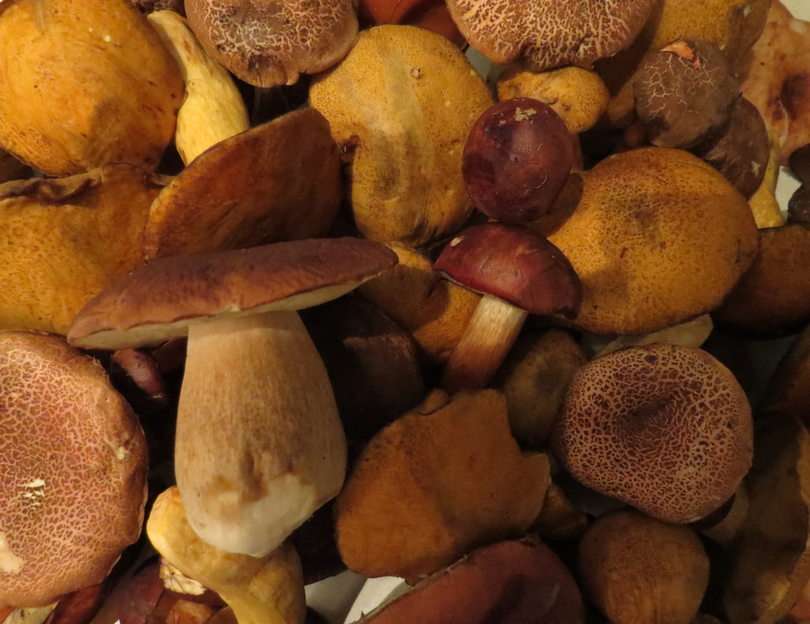
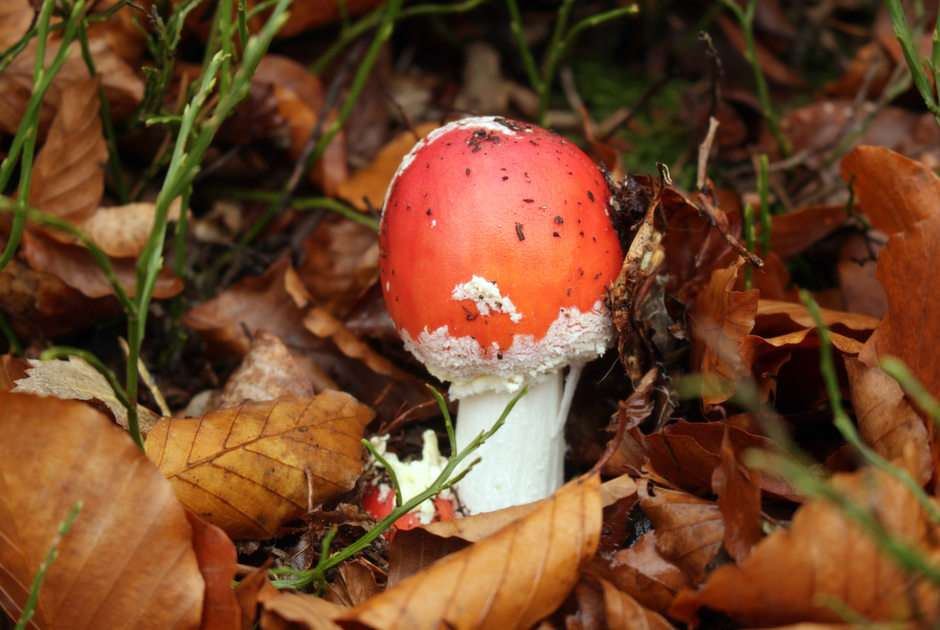
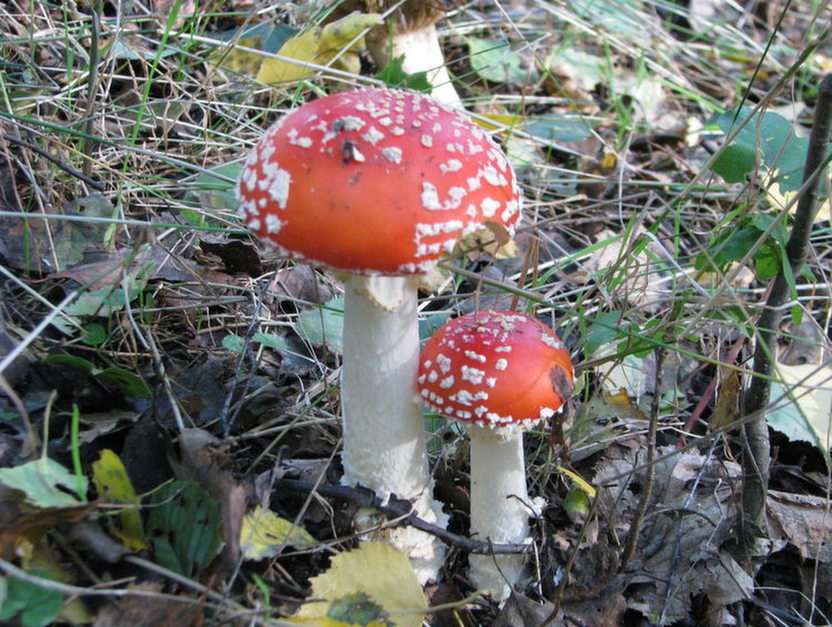
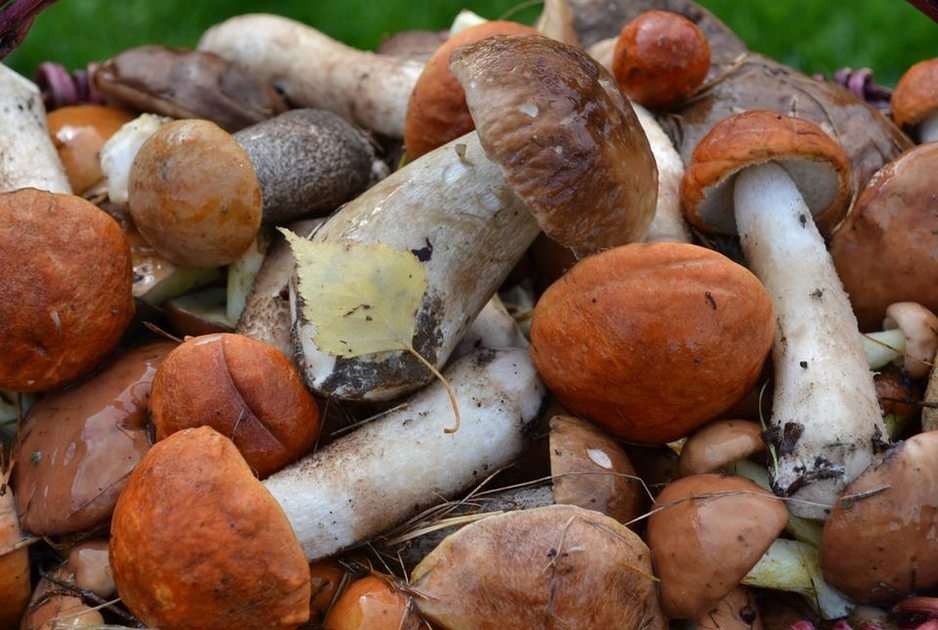
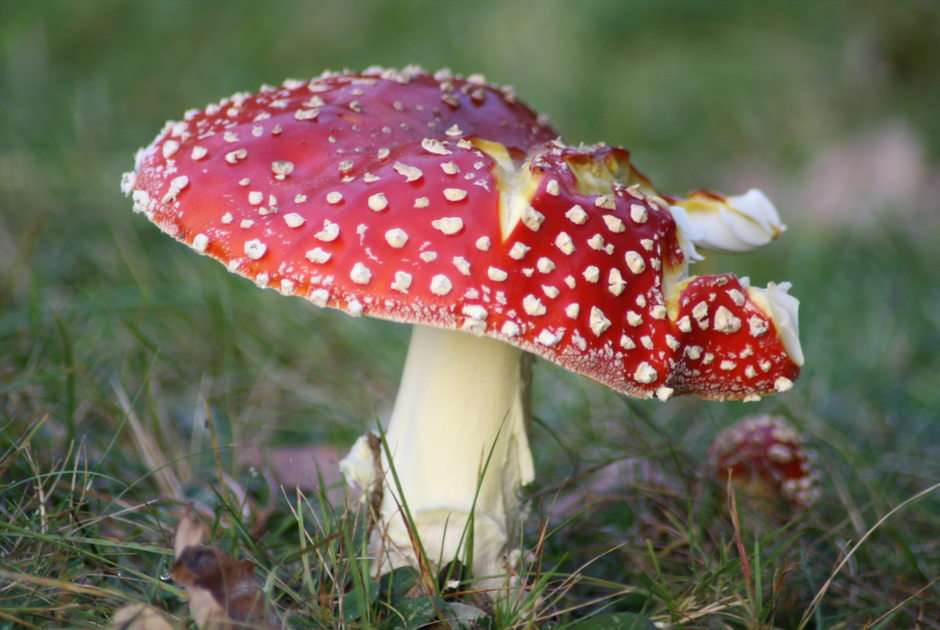
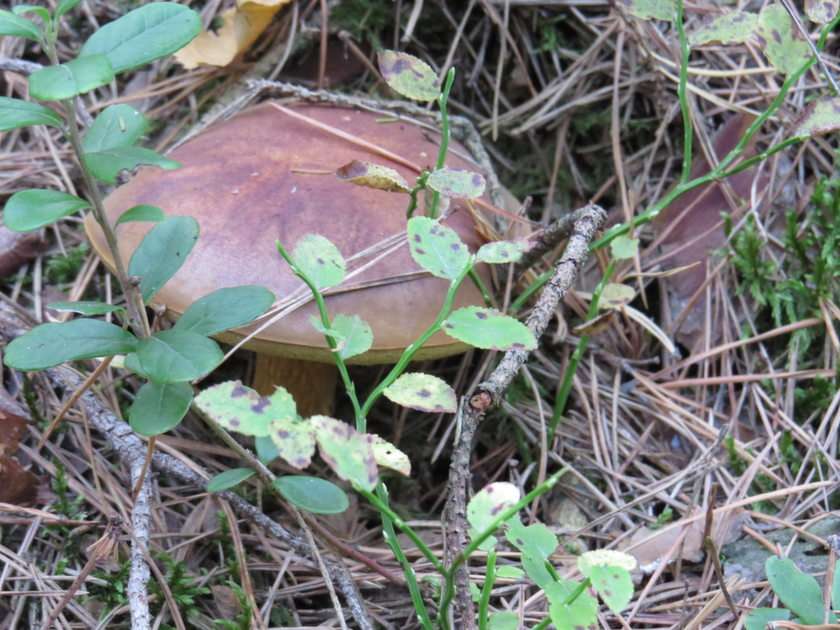
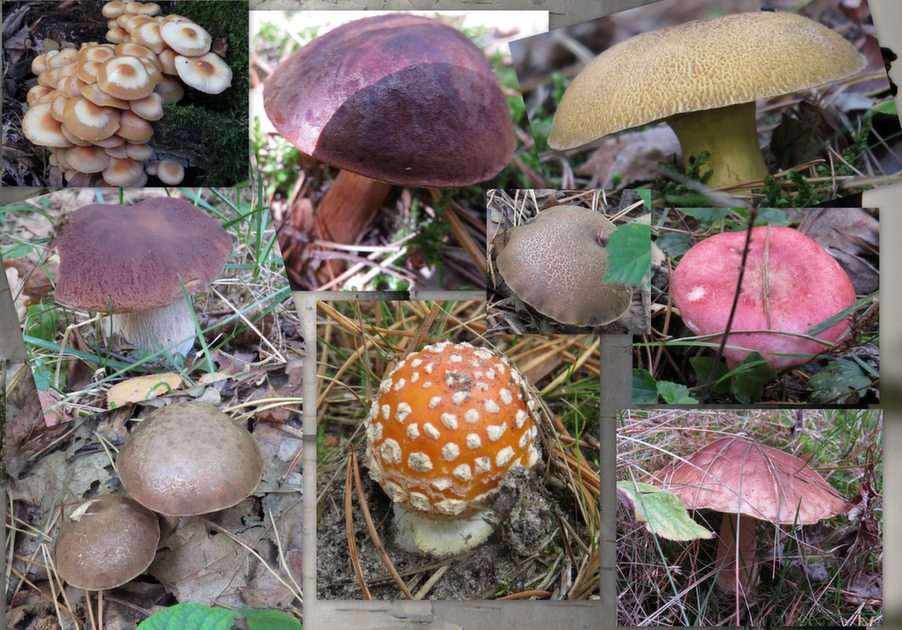
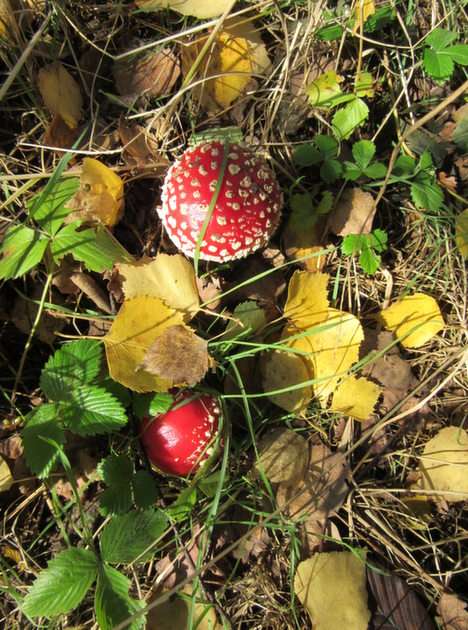
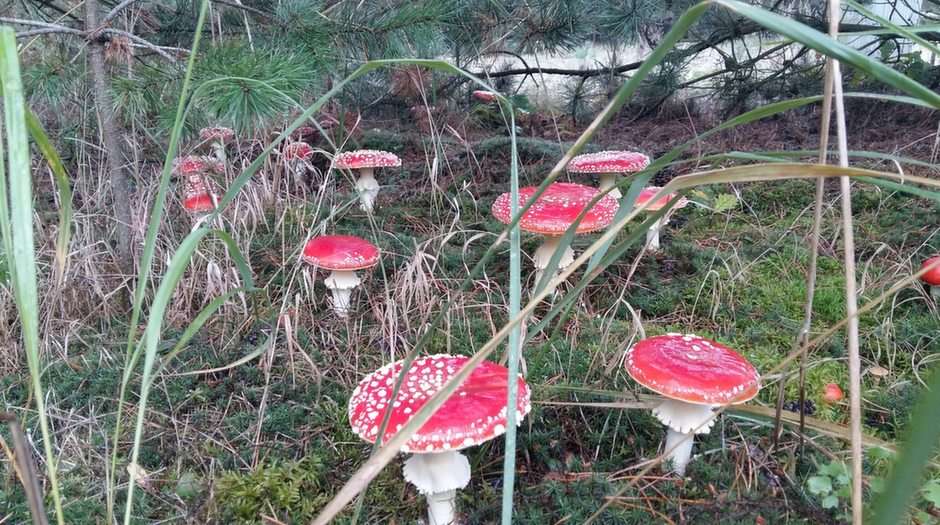
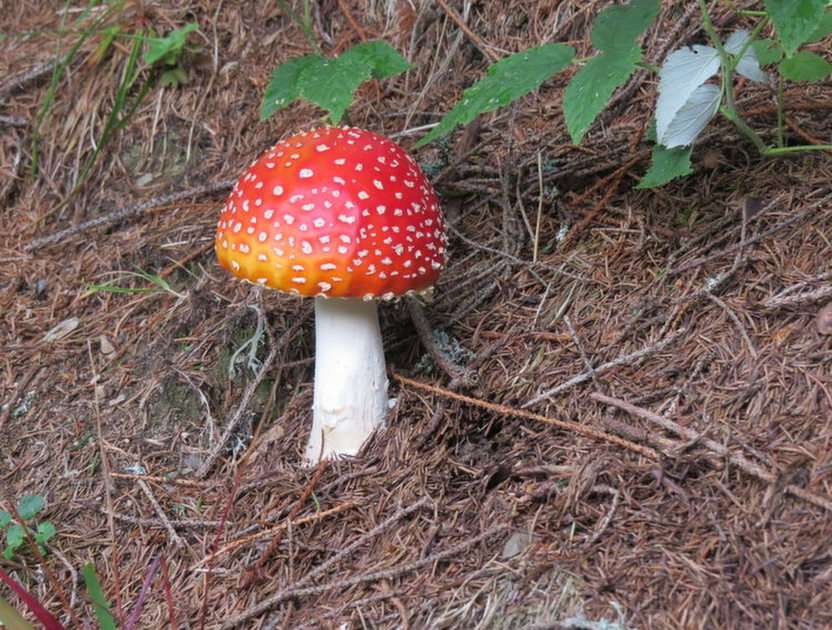
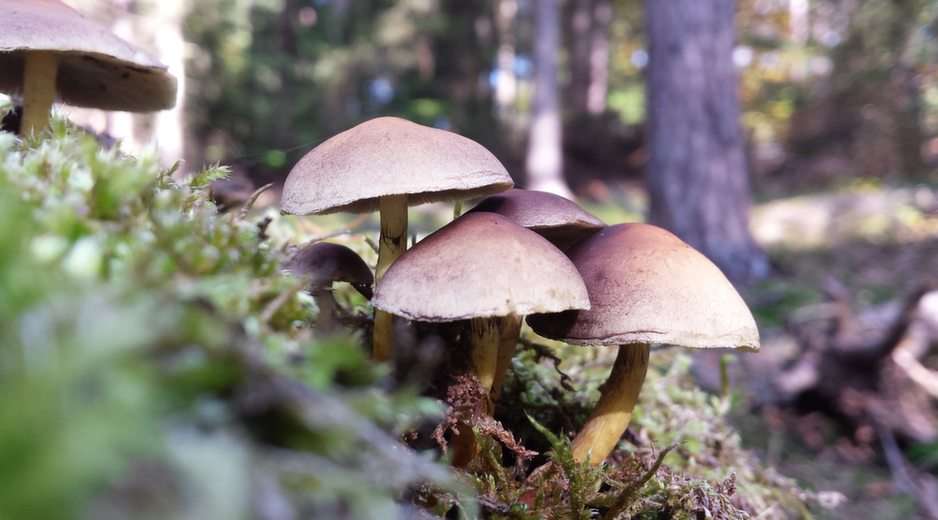
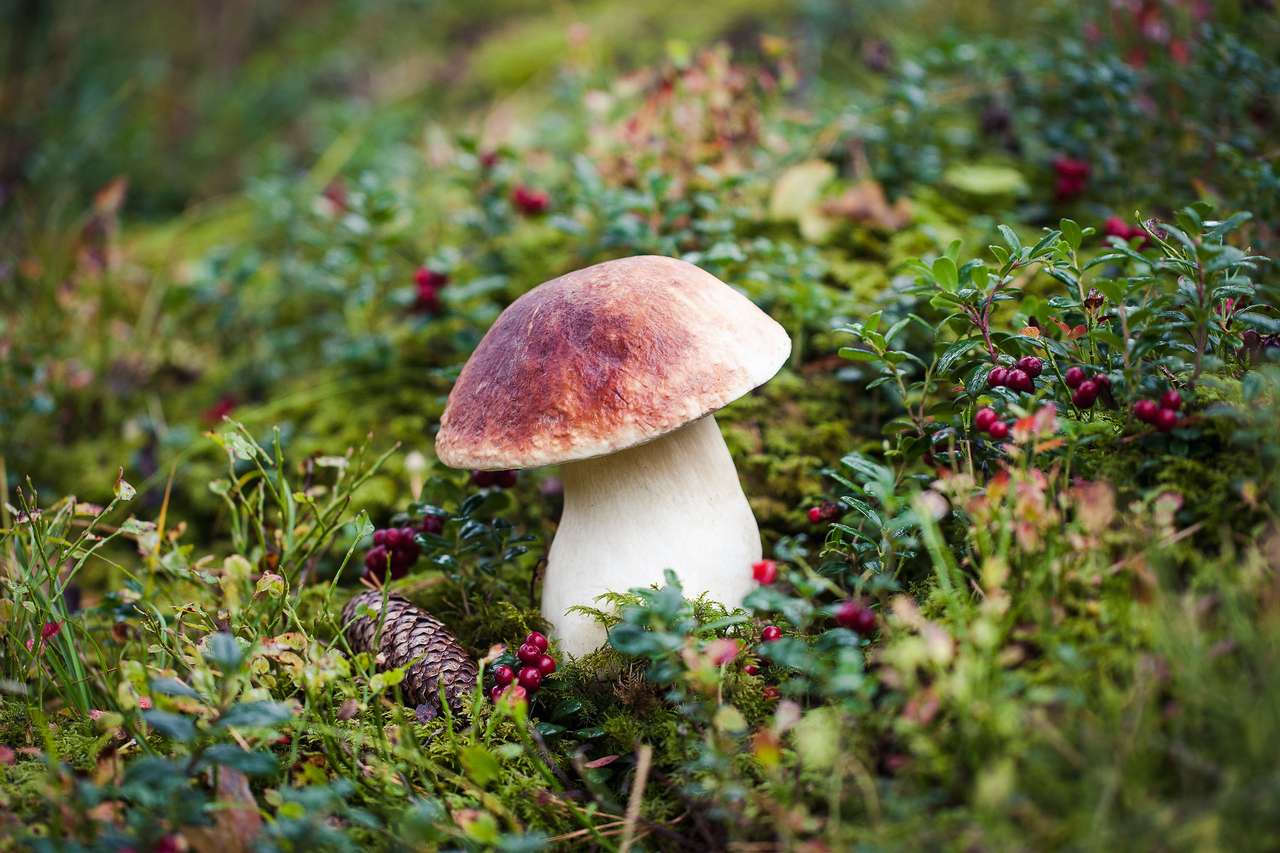
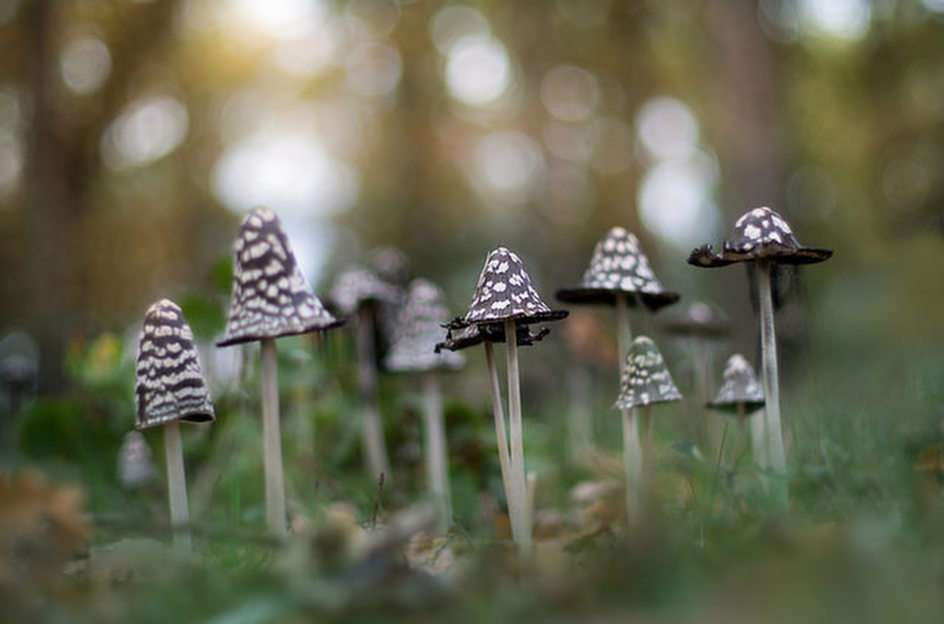





















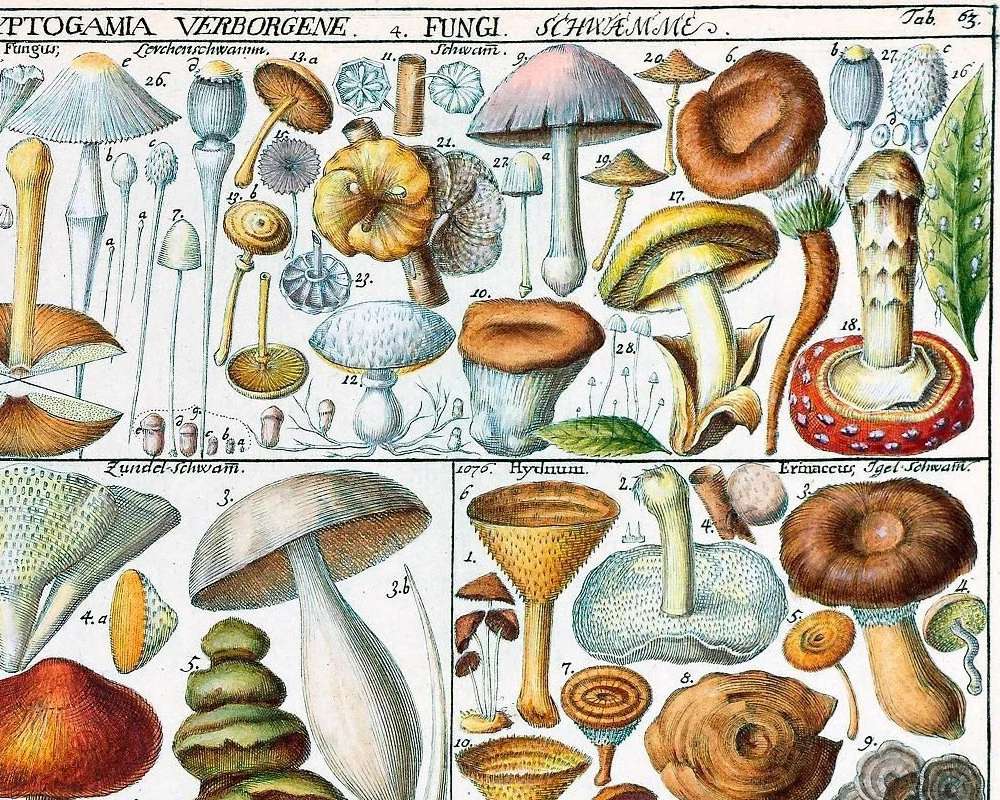
































Online puzzle Fungus
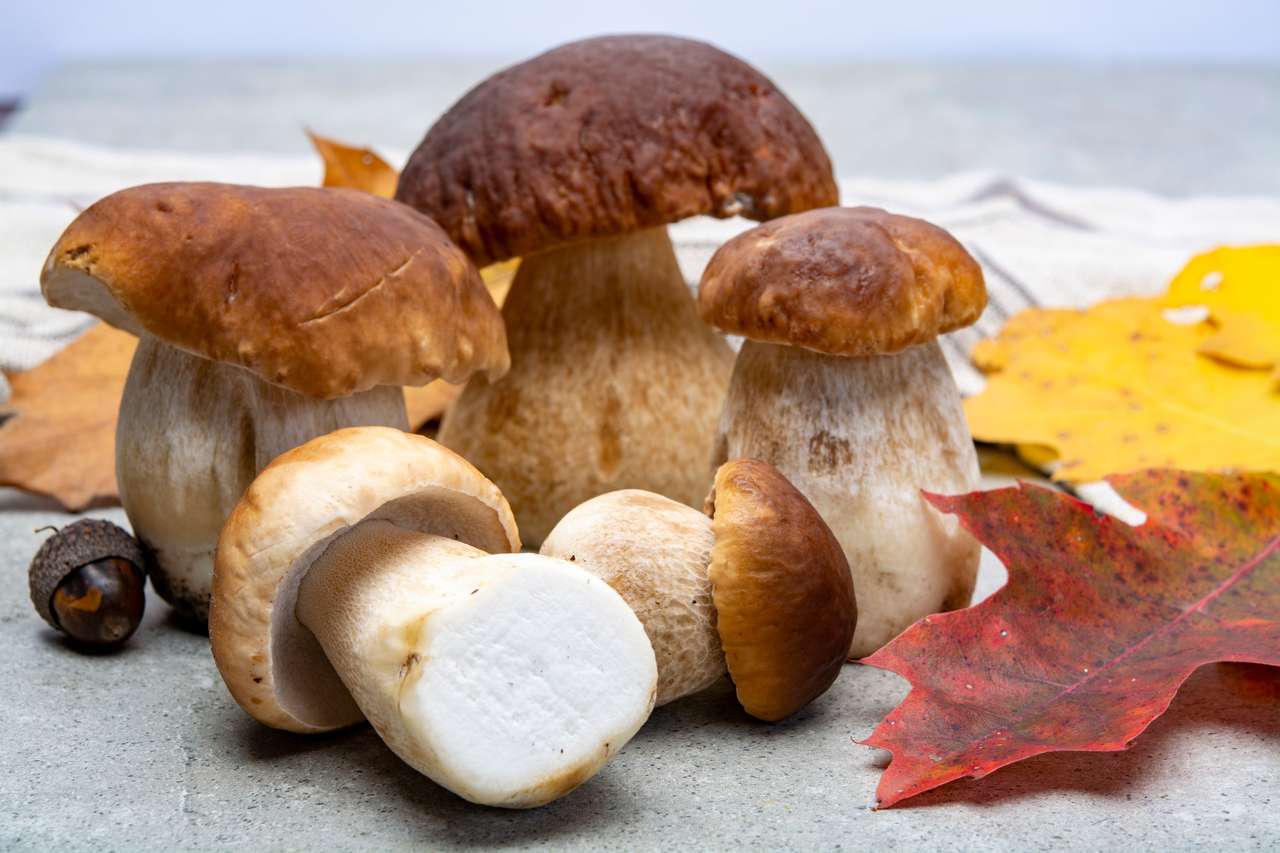
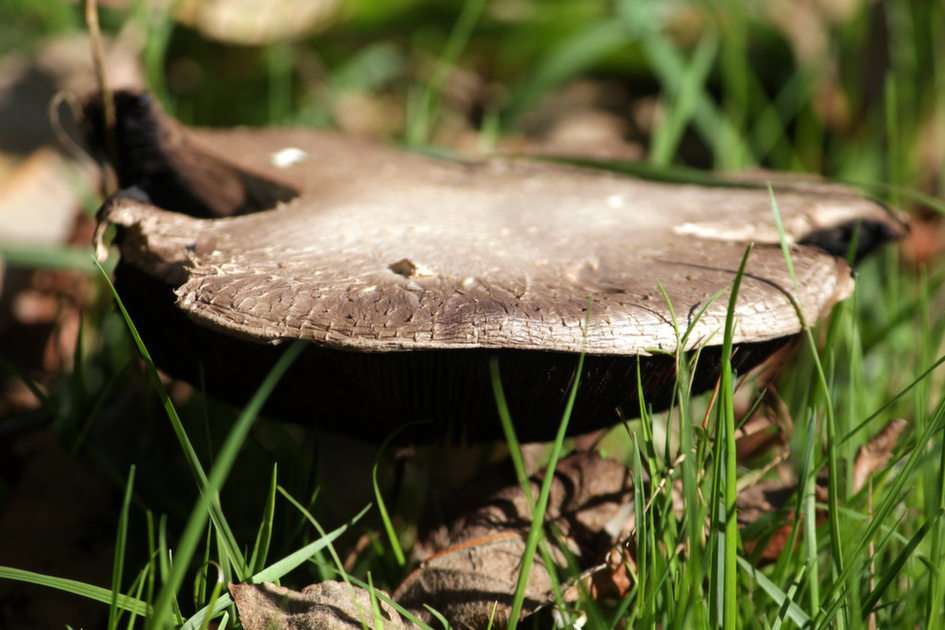
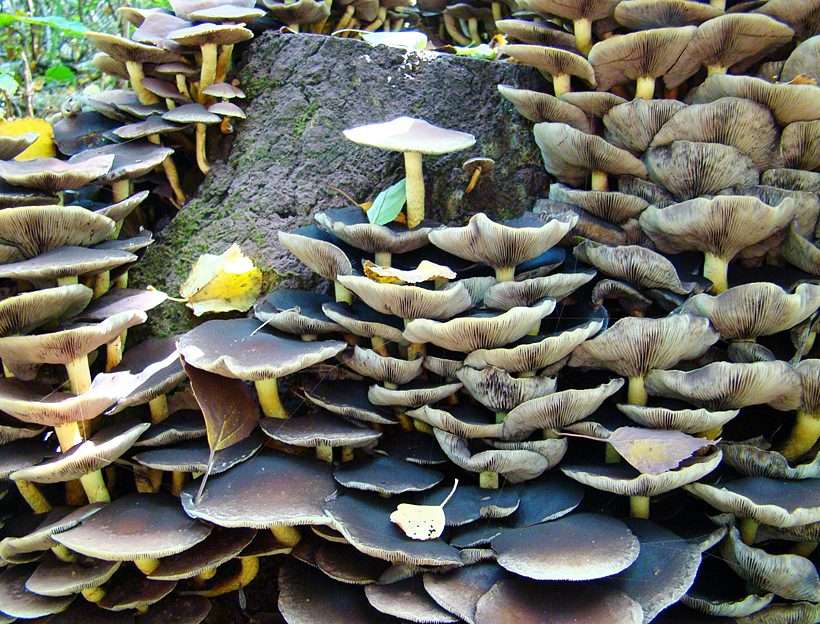
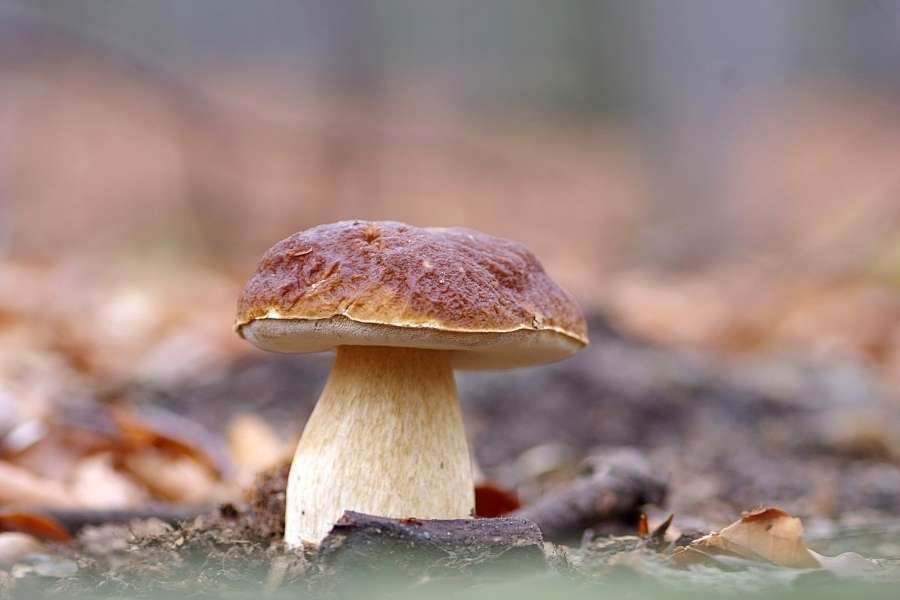
Fungus
A fungus (PL: fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which, by one traditional classification, includes Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista.
A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the Eumycota (true fungi or Eumycetes), that share a common ancestor (i.e. they form a monophyletic group), an interpretation that is also strongly supported by molecular phylogenetics. This fungal group is distinct from the structurally similar myxomycetes (slime molds) and oomycetes (water molds). The discipline of biology devoted to the study of fungi is known as mycology (from the Greek μύκης mykes, mushroom). In the past mycology was regarded as a branch of botany, although it is now known that fungi are genetically more closely related to animals than to plants.
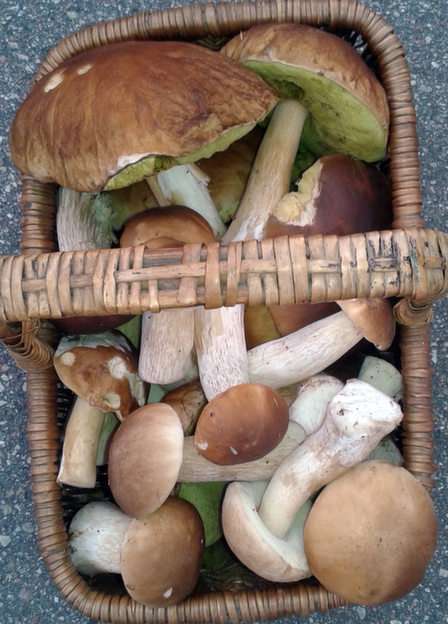
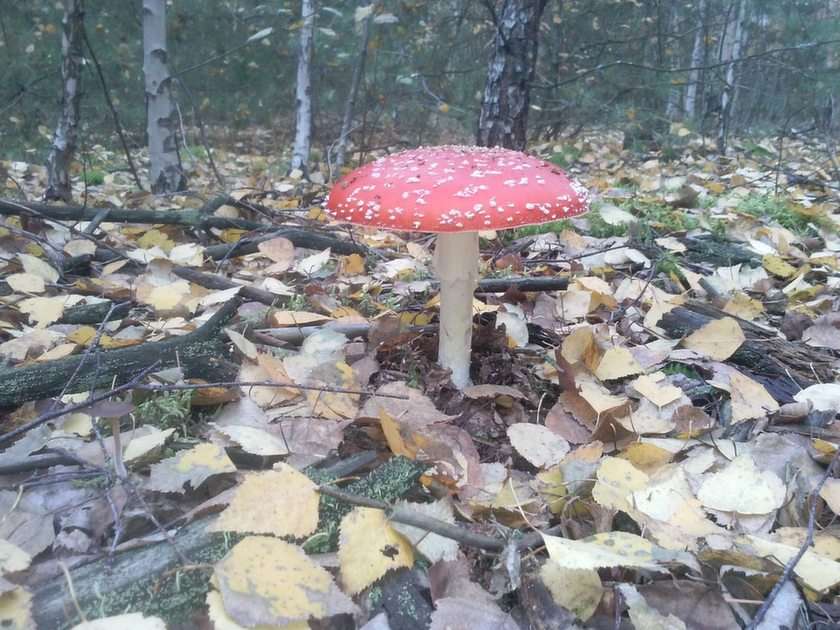
Abundant worldwide, most fungi are inconspicuous because of the small size of their structures, and their cryptic lifestyles in soil or on dead matter. Fungi include symbionts of plants, animals, or other fungi and also parasites. They may become noticeable when fruiting, either as mushrooms or as molds. Fungi perform an essential role in the decomposition of organic matter and have fundamental roles in nutrient cycling and exchange in the environment. They have long been used as a direct source of human food, in the form of mushrooms and truffles; as a leavening agent for bread; and in the fermentation of various food products, such as wine, beer, and soy sauce. Since the 1940s, fungi have been used for the production of antibiotics, and, more recently, various enzymes produced by fungi are used industrially and in detergents. Fungi are also used as biological pesticides to control weeds, plant diseases, and insect pests. Many species produce bioactive compounds called mycotoxins, such as alkaloids and polyketides, that are toxic to animals, including humans. The fruiting structures of a few species contain psychotropic compounds and are consumed recreationally or in traditional spiritual ceremonies. Fungi can break down manufactured materials and buildings, and become significant pathogens of humans and other animals. Losses of crops due to fungal diseases (e.g., rice blast disease) or food spoilage can have a large impact on human food supplies and local economies.
The fungus kingdom encompasses an enormous diversity of taxa with varied ecologies, life cycle strategies, and morphologies ranging from unicellular aquatic chytrids to large mushrooms. However, little is known of the true biodiversity of the fungus kingdom, which has been estimated at 2.2 million to 3.8 million species. Of these, only about 148,000 have been described, with over 8,000 species known to be detrimental to plants and at least 300 that can be pathogenic to humans. Ever since the pioneering 18th and 19th century taxonomical works of Carl Linnaeus, Christiaan Hendrik Persoon, and Elias Magnus Fries, fungi have been classified according to their morphology (e.g., characteristics such as spore color or microscopic features) or physiology. Advances in molecular genetics have opened the way for DNA analysis to be incorporated into taxonomy, which has sometimes challenged the historical groupings based on morphology and other traits. Phylogenetic studies published in the first decade of the 21st century have helped reshape the classification within the fungi kingdom, which is divided into one subkingdom, seven phyla, and ten subphyla.