Engine - online puzzles



















































Online puzzle Engine
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power generation), heat energy (e.g. geothermal), chemical energy, electric potential and nuclear energy (from nuclear fission or nuclear fusion). Many of these processes generate heat as an intermediate energy form, so heat engines have special importance. Some natural processes, such as atmospheric convection cells convert environmental heat into motion (e.g. in the form of rising air currents). Mechanical energy is of particular importance in transportation, but also plays a role in many industrial processes such as cutting, grinding, crushing, and mixing.
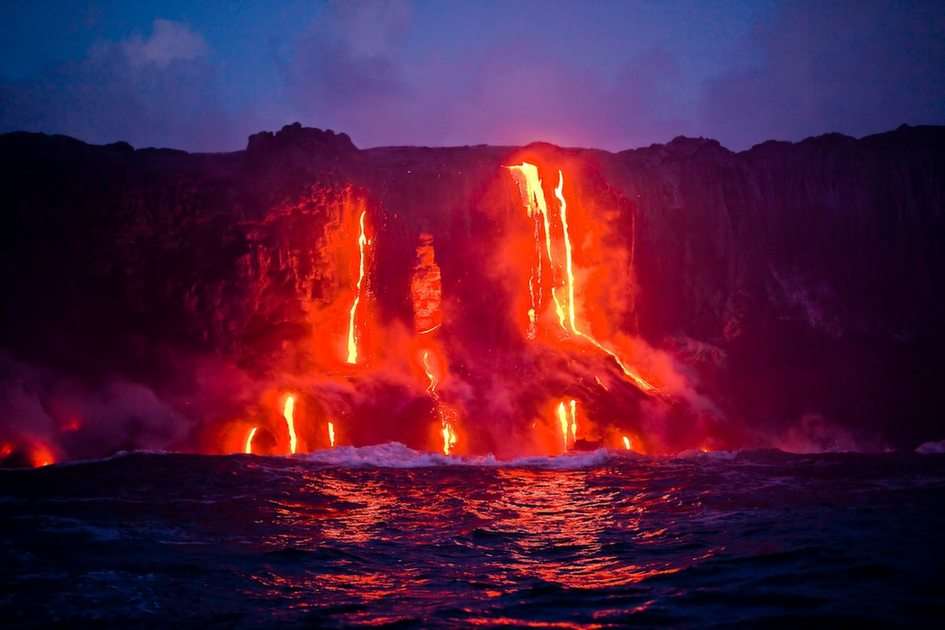
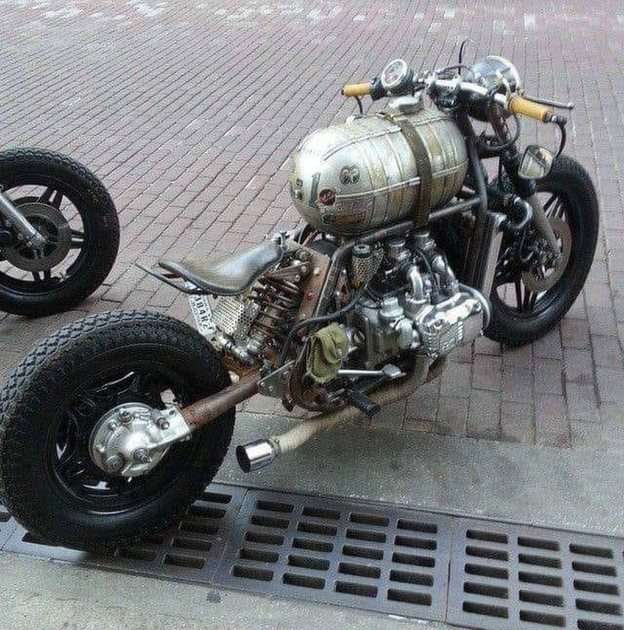
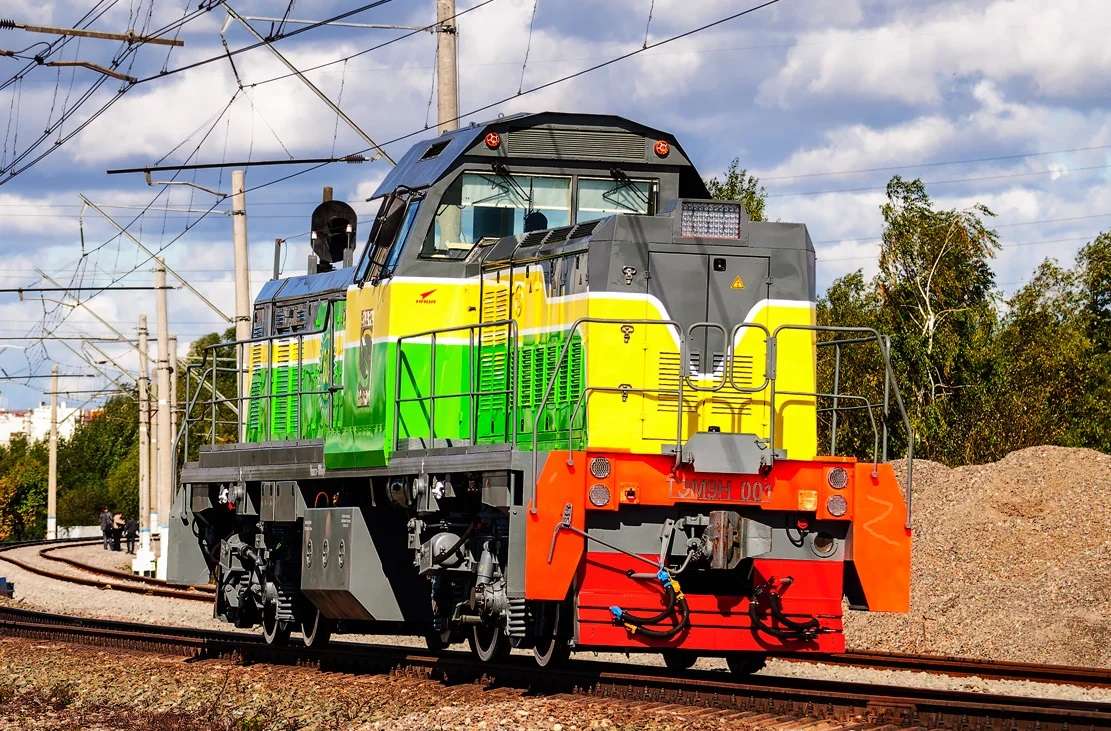
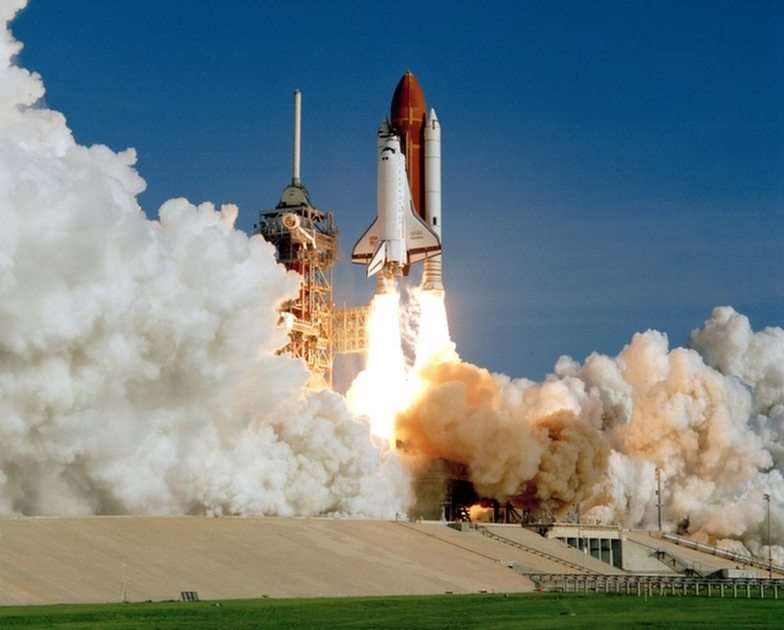
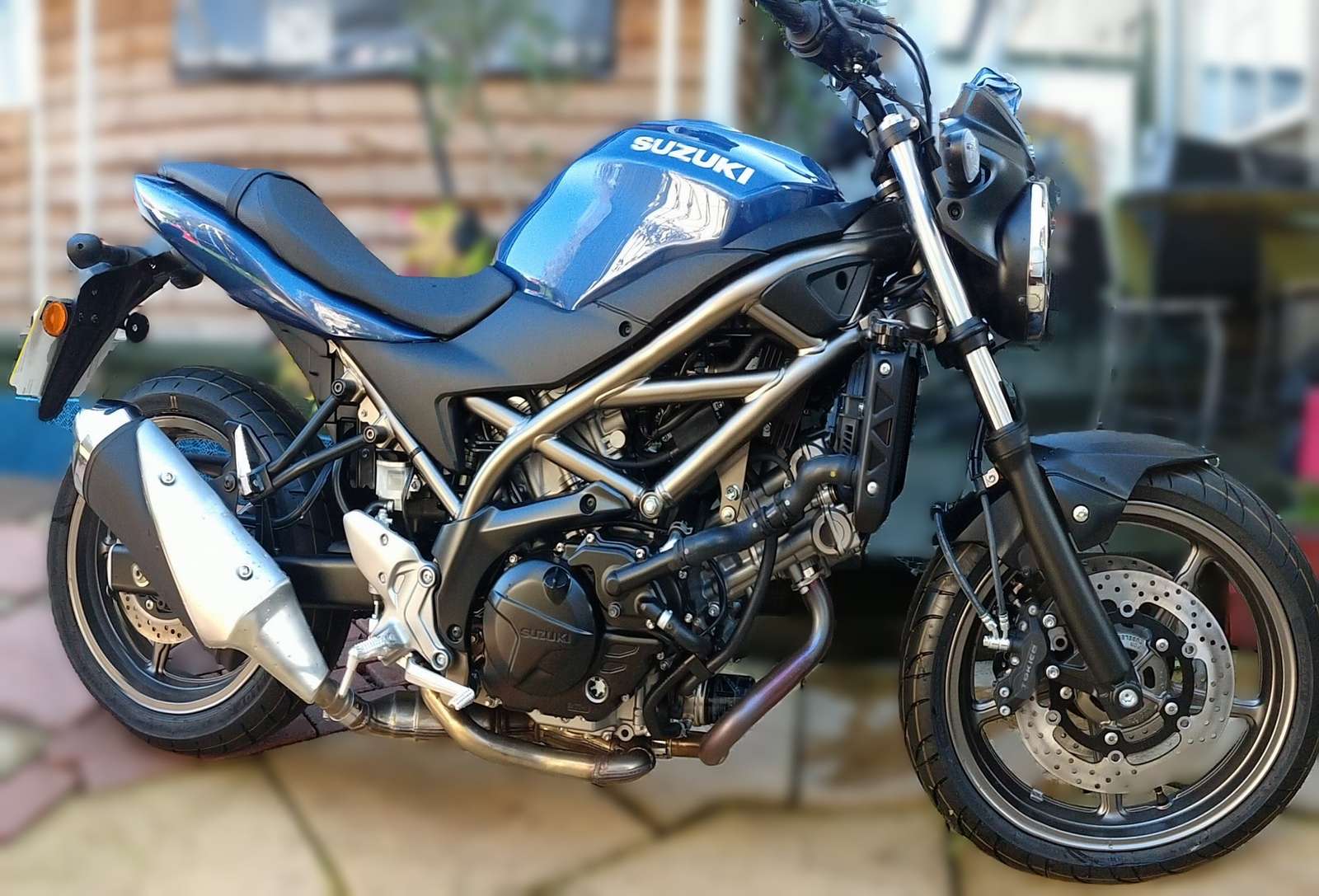
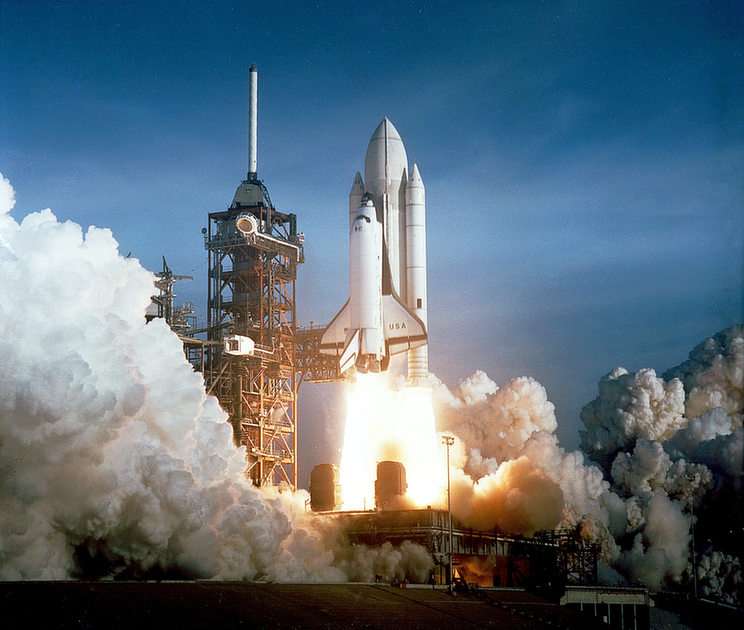
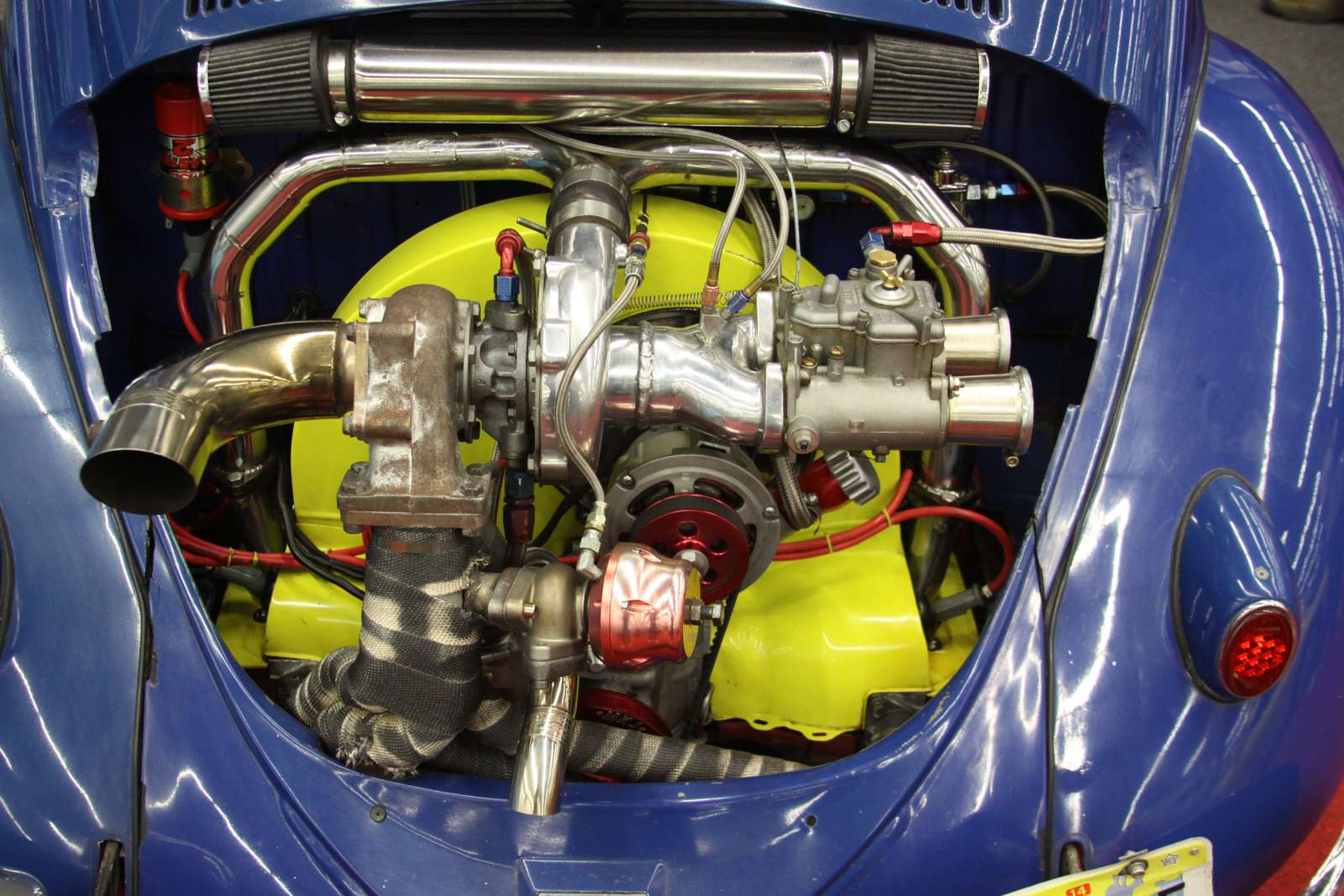
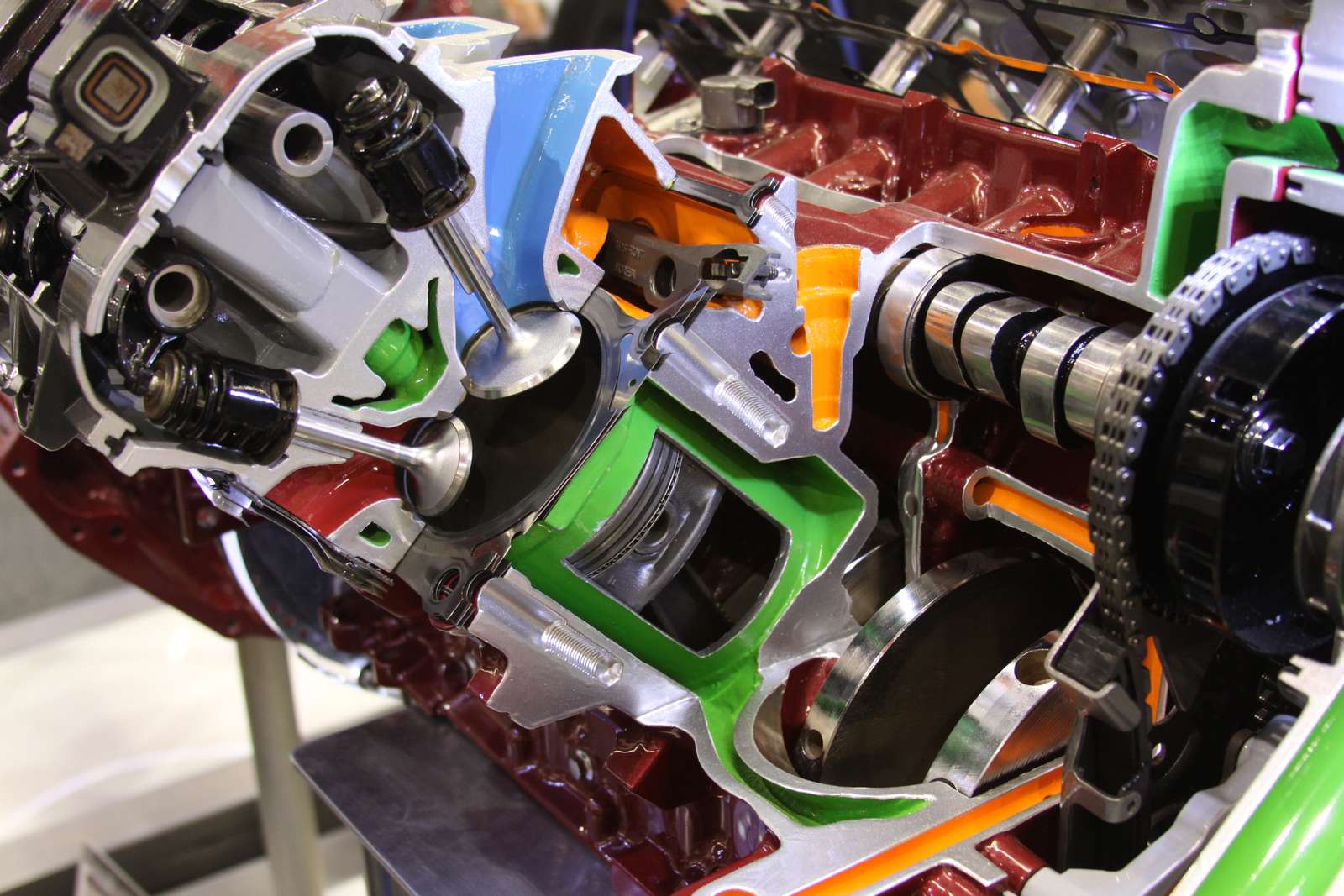
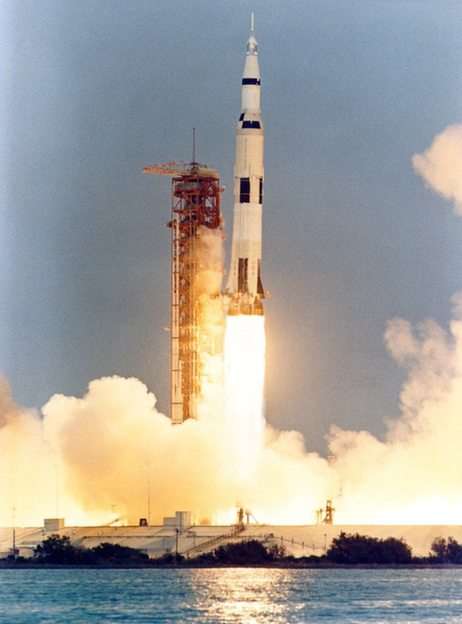
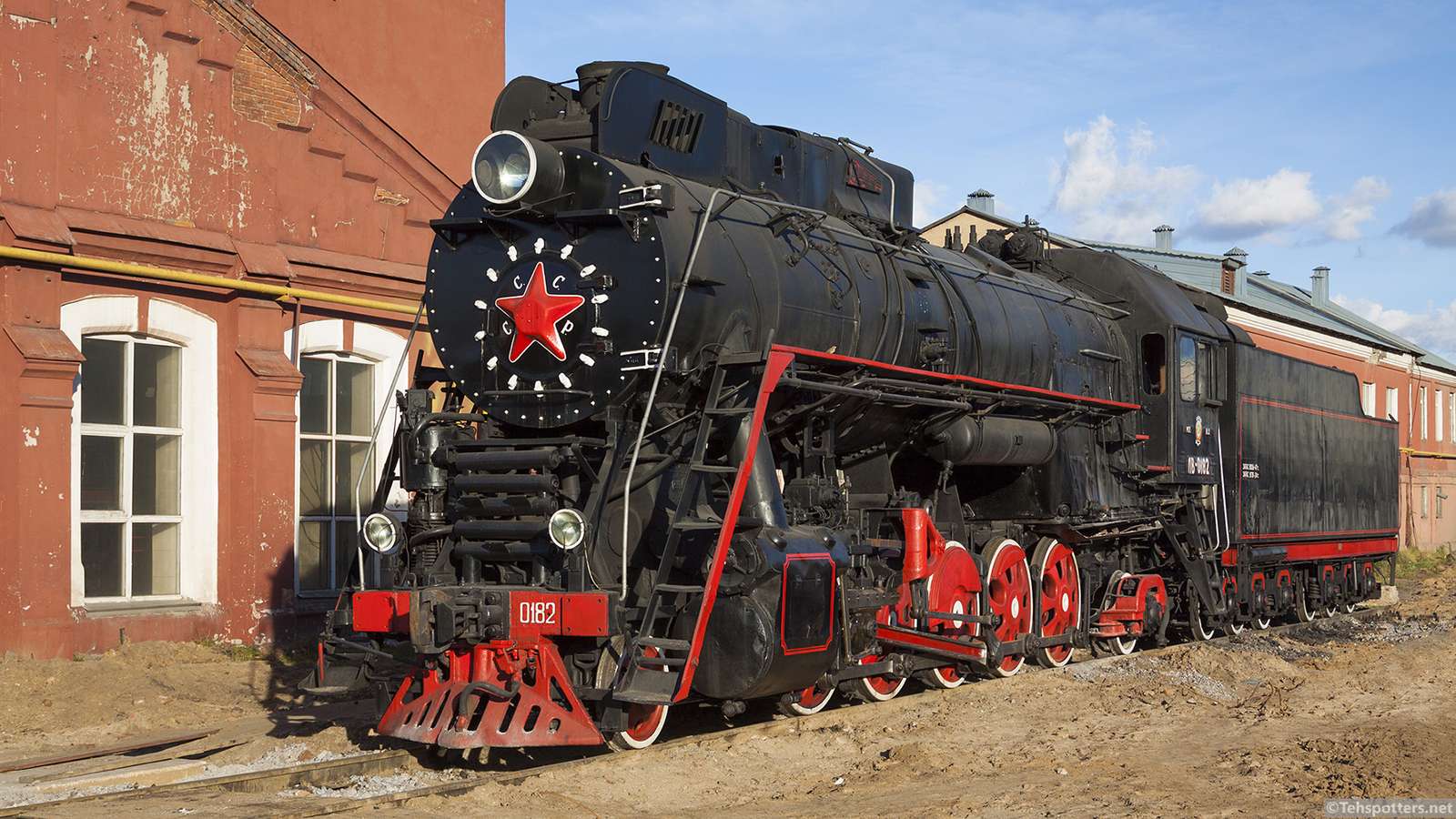
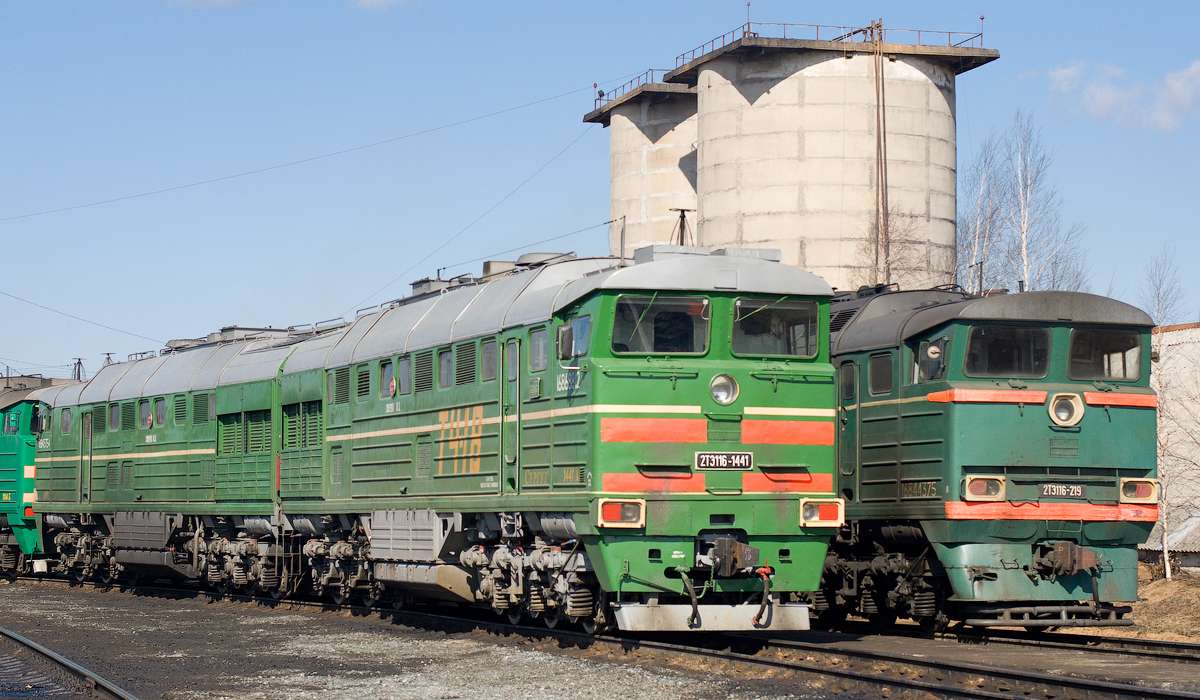
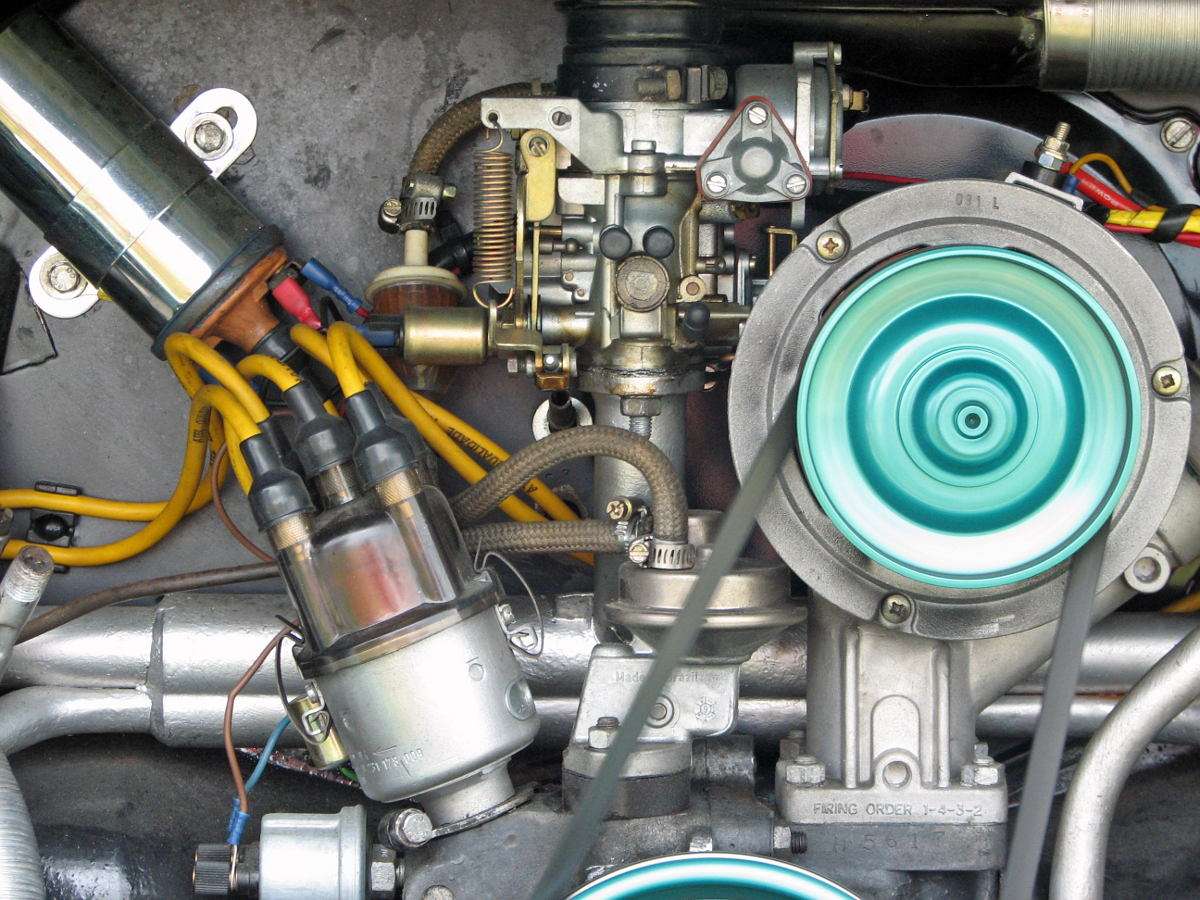
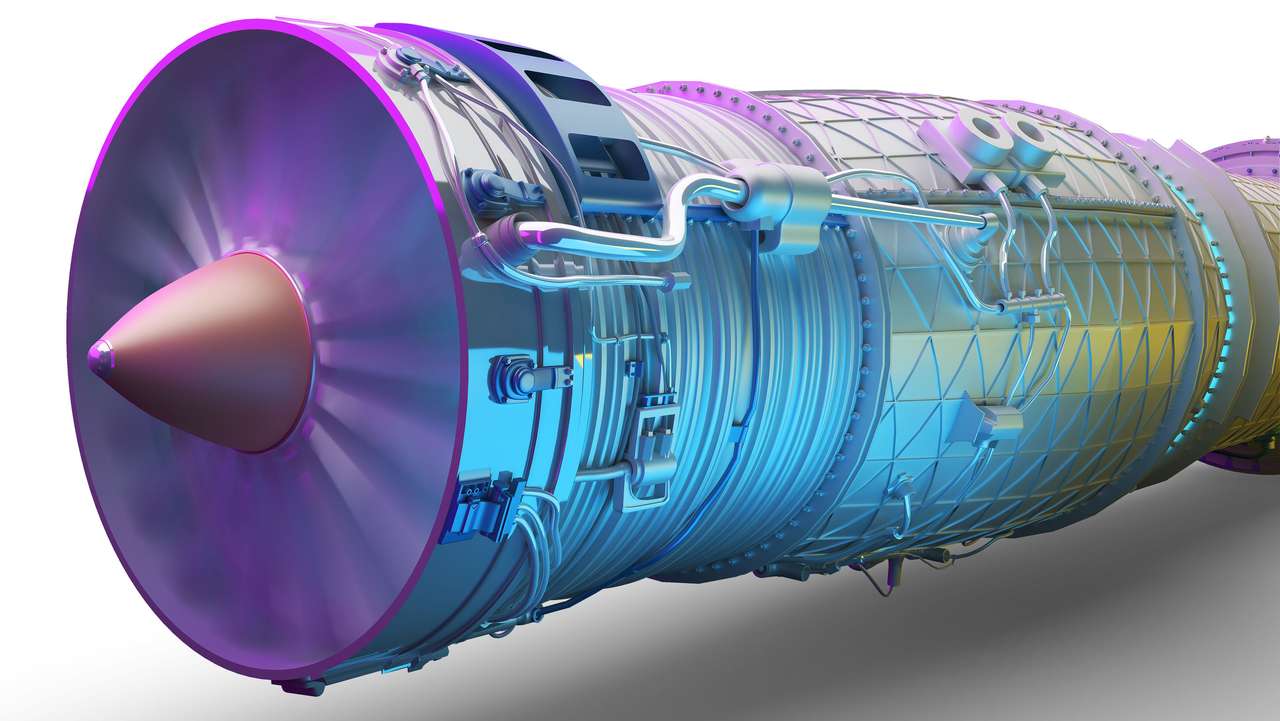
Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a mechanical heat engine, in which heat from the combustion of a fuel causes rapid pressurisation of the gaseous combustion products in the combustion chamber, causing them to expand and drive a piston, which turns a crankshaft. Unlike internal combustion engines, a reaction engine (such as a jet engine) produces thrust by expelling reaction mass, in accordance with Newton's third law of motion.
Apart from heat engines, electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, pneumatic motors use compressed air, and clockwork motors in wind-up toys use elastic energy. In biological systems, molecular motors, like myosins in muscles, use chemical energy to create forces and ultimately motion (a chemical engine, but not a heat engine).
Chemical heat engines which employ air (ambient atmospheric gas) as a part of the fuel reaction are regarded as airbreathing engines. Chemical heat engines designed to operate outside of Earth's atmosphere (e.g. rockets, deeply submerged submarines) need to carry an additional fuel component called the oxidizer (although there exist super-oxidizers suitable for use in rockets, such as fluorine, a more powerful oxidant than oxygen itself); or the application needs to obtain heat by non-chemical means, such as by means of nuclear reactions.
